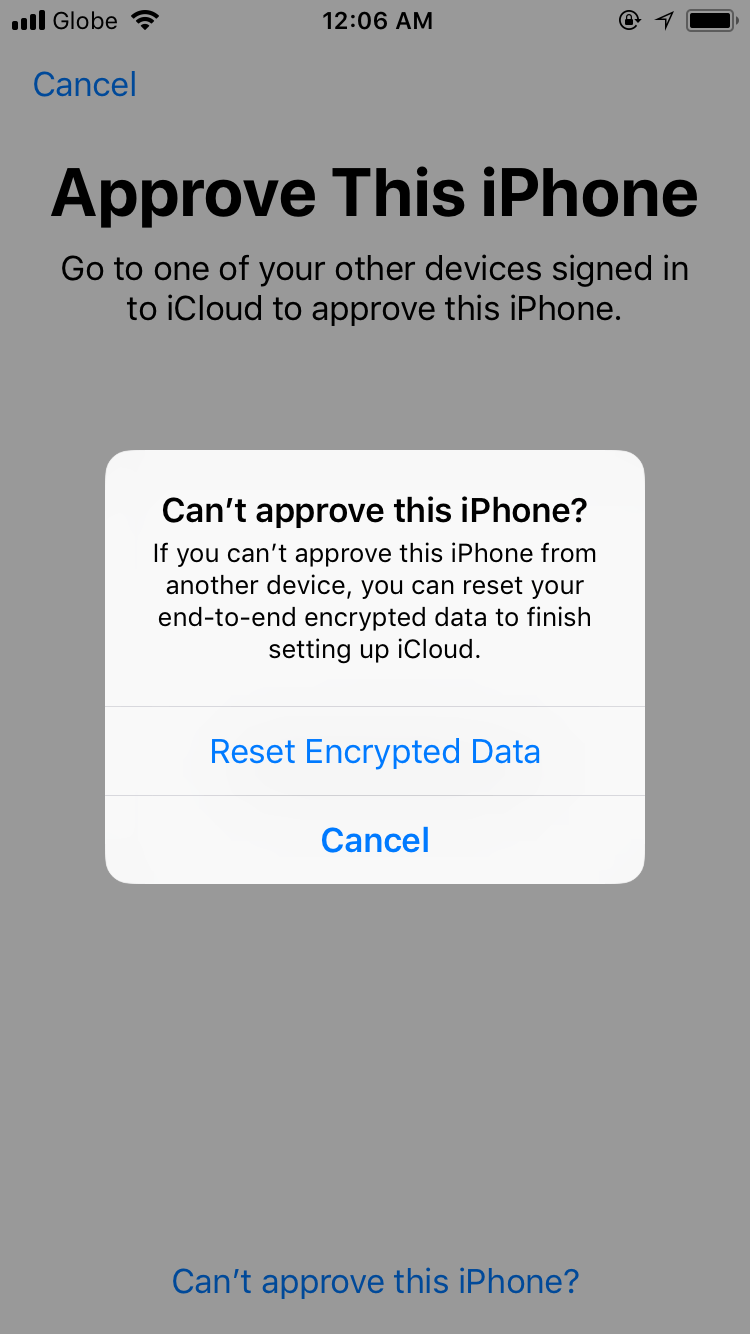
In the world of data security, encryption plays a crucial role in keeping information safe and confidential. But have you ever wondered what happens when you need to reset encrypted data?
Well, you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of resetting encrypted data and why it’s an important process to understand.
Resetting encrypted data is like hitting the reset button on a secret code that keeps your information locked away. It’s a way to start fresh and regain access to encrypted data when something goes wrong. But how does it work? We’ll dive into the details and explain the steps involved in resetting encrypted data.
So, whether you’re curious about data security or just want to learn something new, join us on this journey to discover the fascinating world of resetting encrypted data! Get ready to unravel the mysteries and gain a deeper understanding of this vital process.
What is Resetting Encrypted Data
Resetting encrypted data involves restoring encrypted information to its original state. This process typically requires the use of an encryption key to decrypt the data, making it readable again.
It’s an essential step when data needs to be accessed or modified. Resetting encrypted data ensures data integrity and security while allowing authorized users to work with the information.
By understanding how to reset encrypted data, you can effectively manage and protect sensitive information in various systems and applications.
Why Resetting Encrypted Data Is Important?
Resetting encrypted data plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information. Encrypted data refers to data that has been transformed using an algorithm to become unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
This ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the data, they are unable to decipher its meaning. However, the encryption process is not foolproof, and there are occasions when resetting encrypted data becomes necessary.
One of the key reasons for resetting encrypted data is when an encryption key becomes compromised. Encryption keys are used to lock and unlock encrypted data, and if a key is compromised, it poses a significant security risk.
In such cases, resetting the encrypted data involves generating a new encryption key and re-encrypting the data with the new key, rendering the compromised key useless. This ensures that any unauthorized individuals who may have gained access to the compromised key are unable to decrypt the data.
Resetting encrypted data is crucial when data needs to be securely transferred or shared. By resetting the encryption, a new key can be generated specifically to share the data and ensure that only intended recipients can access and decrypt the information. This adds an extra layer of security and control over sensitive data.
Process of Resetting Encrypted Data
When it comes to resetting encrypted data, the process typically involves several steps to ensure the security and integrity of the data. Let’s explore the key components of this process:
1. Assessing the Need for Reset: The first step is to determine whether resetting the encrypted data is necessary. This assessment is usually based on factors such as the compromise of encryption keys, the need for secure data transfer, or the expiration of encryption keys.
2. Generating a New Encryption Key: If the need for resetting is identified, the next step is to generate a new encryption key. This key will replace the compromised or outdated key and will be used to encrypt the data.
3. Decrypting and Re-encrypting the Data: Once the new encryption key is generated, the previously encrypted data must be decrypted using the old key. This decrypted data is then re-encrypted using the new encryption key, ensuring that it remains protected.
4. Updating Access Controls: As part of the resetting process, it is essential to update the access controls for the newly encrypted data. This ensures that only authorized users with the appropriate decryption key can access the data.
5. Securely Disposing of Old Keys: Finally, the old encryption keys should be securely disposed of to prevent any potential misuse. This may involve physical destruction or secure deletion methods.
Benefits of Resetting Encrypted Data
Resetting encrypted data brings a range of benefits that contribute to overall data security. Here are a few key advantages:
1. Protection from Compromised Keys: By resetting encrypted data, any risk associated with compromised encryption keys is mitigated. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to an old or compromised key, they are unable to decrypt the data.
2. Enhanced Data Privacy: Resetting encrypted data allows for the implementation of stronger encryption algorithms and more secure encryption keys, leading to enhanced data privacy and confidentiality.
3. Control over Data Access: By resetting encrypted data, organizations gain greater control over who can access and decrypt certain data. This is particularly important when sharing sensitive information with external parties.
4. Compliance with Data Security Regulations: Many industries and jurisdictions have specific regulations regarding the protection of sensitive data. By resetting encrypted data and ensuring appropriate security measures, organizations can maintain compliance with these regulations.
5. Confidence in Data Integrity: Resetting encrypted data helps maintain the integrity of the information. It ensures that only authorized individuals can access and modify the data, reducing the risk of unauthorized tampering.
Things To Do and Not To Do while Resetting Encrypted Data
When it comes to resetting encrypted data, following best practices is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the process. Here are some dos and don’ts to keep in mind:
Do:
- Regularly assess the need to reset encrypted data to prevent potential security breaches.
- Use strong encryption algorithms and regularly update encryption keys for maximum security.
- Implement access controls to restrict data accessibility to authorized individuals only.
- Dispose of old encryption keys securely to prevent any potential misuse.
- Maintain compliance with relevant data security regulations and standards.
Don’t:
- Reset encrypted data without a valid reason or thorough assessment.
- Delay the resetting process if encryption keys are compromised or outdated.
- Overlook the importance of access controls and user authentication when resetting encrypted data.
- Underestimate the importance of proper disposal of old encryption keys.
- Ignore or neglect data security regulations specific to your industry or jurisdiction.
Best Practices for Resetting Encrypted Data
When it comes to resetting encrypted data, following best practices is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the process. Here are some key best practices to consider:
1. Regularly Assess Encryption Key Security
Regularly evaluating the security of your encryption keys is essential to identify any potential compromises. This assessment can involve monitoring key usage, detecting unusual activity, or conducting periodic audits.
2. Use Strong and Up-to-Date Encryption Algorithms
Ensure that your encryption algorithms are robust and up-to-date. Staying current with the latest encryption standards and technologies helps maintain the confidentiality of your encrypted data and protects against emerging threats.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Adding an additional layer of security through multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance the protection of your encrypted data. By requiring multiple forms of identification, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens, you reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
4. Regularly Update Encryption Keys
To maintain the highest level of security, periodically update your encryption keys. This practice ensures that even if an encryption key is compromised, its lifespan is limited, reducing the potential impact on the security of your data.
5. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encrypting data both at rest (stored on devices or servers) and in transit (during transfer) ensures that your sensitive information remains protected at all times. This comprehensive approach strengthens your data security posture.
6. Train Employees on Data Security Protocols
One of the weakest links in data security is human error. Train your employees on best practices for data security, including the proper handling of encryption keys, password security, and the recognition of potential threats or phishing attempts.
Resetting encrypted data is a vital aspect of maintaining the security and integrity of sensitive information. By understanding the importance of resetting encrypted data, the process involved, and best practices, individuals and organizations can enhance their data security measures.
Remember to regularly assess the need for resetting, generate strong encryption keys, and implement access controls to ensure the utmost protection of your encrypted data. By following these guidelines, you can confidently navigate the realm of data security and safeguard your valuable information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Resetting encrypted data is a process of reverting encrypted information back to its original, unencrypted state. It is often done to regain access to encrypted data when the encryption key is lost or forgotten.
Here are some common questions and answers related to resetting encrypted data:
1. How does resetting encrypted data work?
Resetting encrypted data involves using a decryption algorithm or key to reverse the encryption process. When data is encrypted, it is transformed into an unreadable format using a specific algorithm and encryption key. Resetting the encrypted data requires either finding or recreating the original encryption key to decrypt the data and restore it to its original, unencrypted state.
It’s important to note that resetting encrypted data can only be done if you have the necessary authority and access rights to the data. It is a security-sensitive operation that must be handled with caution.
2. When would I need to reset encrypted data?
You may need to reset encrypted data in various scenarios. One common situation is when you forget or lose the encryption key or password that was used to protect the data. Without the key, the encrypted data is essentially inaccessible.
Another instance where resetting encrypted data may be required is during data recovery efforts. If you have encrypted backups or files that need to be restored, resetting the encryption ensures that the data can be accessed and restored to its original form.
3. Is resetting encrypted data permanent?
Resetting encrypted data is typically a permanent process. Once the encryption is reversed and the data is restored to its original form, it remains unencrypted. However, it’s important to consider the security implications of permanently resetting encrypted data.
It is recommended to only reset encrypted data when necessary and to ensure that appropriate security measures, such as re-encrypting the data with a new key, are in place after resetting. This helps maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the data.
4. Can resetting encrypted data be done without the original encryption key?
In most cases, resetting encrypted data without the original encryption key is not possible. The encryption key is crucial in the encryption and decryption processes. Without the key, the encrypted data cannot be properly decrypted and restored to its original form.
However, there may be rare cases where alternative methods or techniques can be used to recover or reset encrypted data without the original encryption key. These methods often require specialized knowledge and tools and may not always be successful. It’s advisable to consult with security experts or professionals in such cases.
5. What are the risks of resetting encrypted data?
Resetting encrypted data carries some inherent risks. One of the main risks is the potential loss of data if the process is not performed correctly or if the wrong encryption key is used. It’s crucial to have proper backups and to double-check the encryption key or password before proceeding with the resetting process.
Additionally, resetting encrypted data may introduce vulnerabilities if the data is not re-encrypted with a new key or if the security measures are not properly implemented. It’s important to consider the overall security implications and to follow best practices when resetting encrypted data.
Resetting encrypted data is like giving a secret code to protect your information. It’s like creating a new secret code to hide your message. Resetting means changing the secret code so that only you can understand it. But be careful, if you forget the new code, you might lose your information forever!
When you reset encrypted data, it’s important to remember your new secret code. If you forget it, the data will be locked forever. So, resetting encrypted data is like changing the lock on your secret diary. Just make sure you don’t forget the new key!