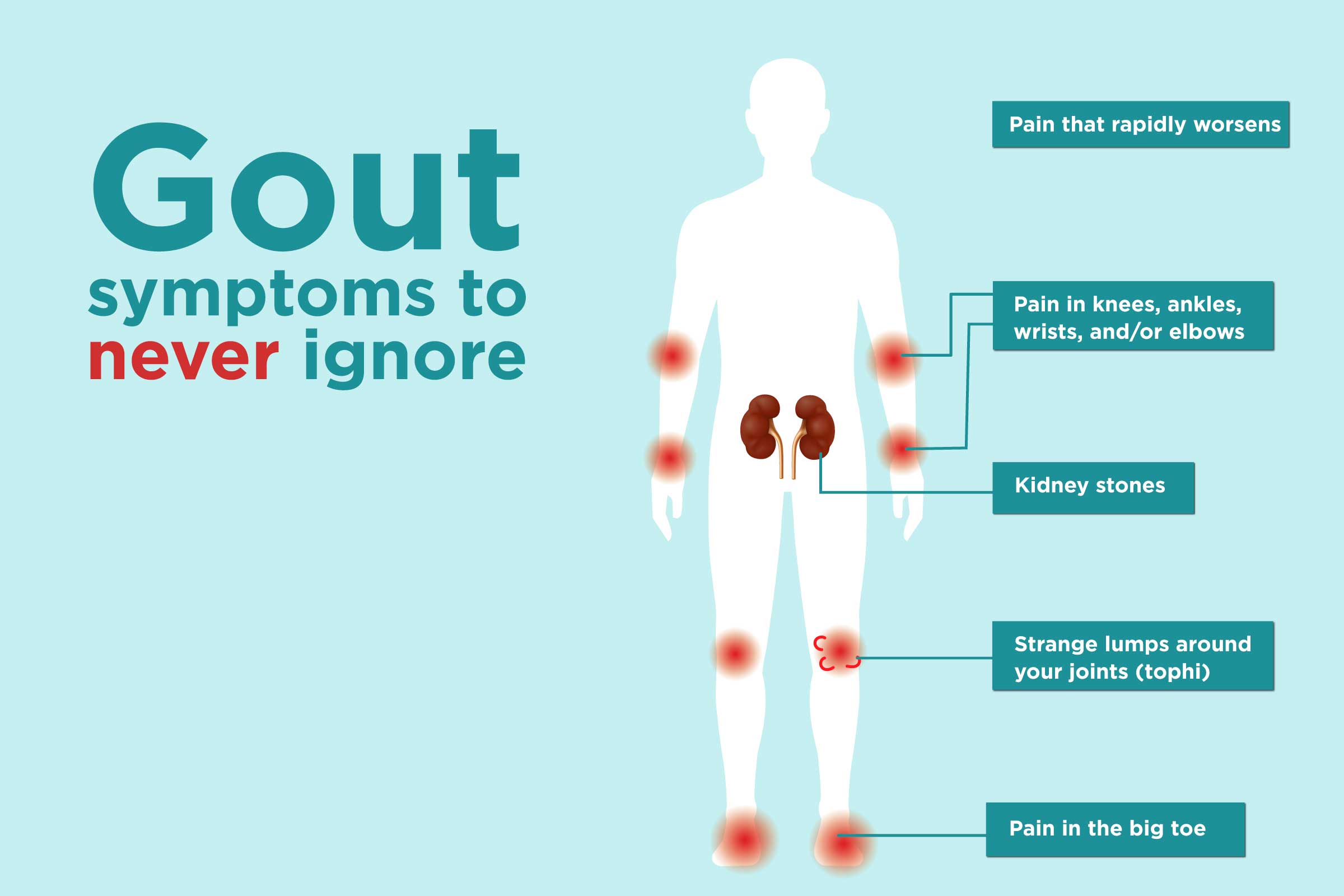
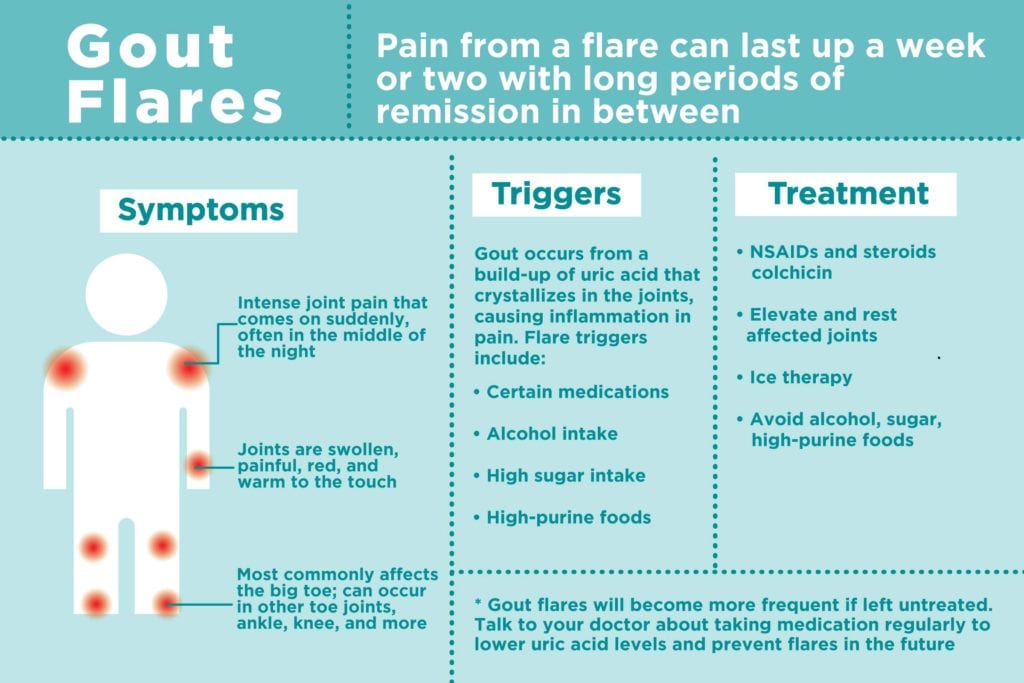
A gout attack is a sudden, severe pain in joints, often the big toe. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and tenderness.
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by high uric acid levels in the blood. Crystals form in the joints, leading to intense pain and inflammation. The big toe is commonly affected, but other joints can suffer too. Gout attacks often occur suddenly, even waking you up at night.
Lifestyle choices, such as diet and alcohol consumption, can influence gout. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms effectively. Understanding the causes and symptoms of gout is crucial for preventing future attacks. Proper medical advice and lifestyle changes are essential for managing this condition.
What is Gout?
Gout has been known for centuries. Ancient Egyptians first identified it. The disease was known as the “disease of kings.” This was because rich people often got it. They ate a lot of meat and drank wine. Both can lead to gout. Famous people like Henry VIII and Benjamin Franklin had gout.
Gout is common today. Many people suffer from it. It affects more men than women. Women usually get it after menopause. Gout is more common in older adults. It affects millions of people worldwide. Changes in diet and lifestyle can help manage gout.
What Is A Gout Attack?
A gout attack is a sudden and intense pain in a joint. It often occurs at night. The affected joint becomes red, hot, and swollen. The pain usually lasts for a few days. Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. This acid forms crystals in the joints. These crystals cause inflammation and pain.
Many people think gout only affects older men. This is not true. Women and younger people can get gout too. Some believe gout is always caused by eating rich foods. While diet can affect gout, it is not the only cause. Genetics play a big role in gout. Many think gout only affects the big toe. Gout can affect any joint in the body.
Symptoms Of Gout
Redness and swelling in the affected joint are common early signs. The area might feel warm to the touch. Pain often starts suddenly and can be intense. It usually begins in the big toe but can occur elsewhere. The pain can wake you up at night. Sometimes, the skin around the joint can look shiny.
The pain may become excruciating, making it hard to move the affected joint. Fever can sometimes occur with severe gout attacks. The joint may become very swollen and extremely tender. Long-lasting discomfort might persist even after the intense pain subsides. Mobility can be significantly reduced during severe attacks.
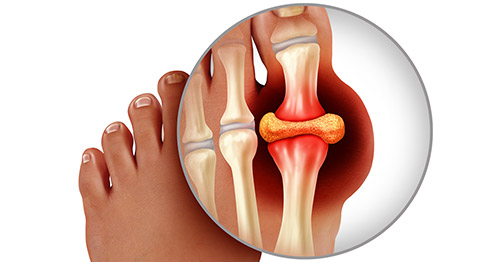
Causes Of Gout
Gout attacks arise from high levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to crystal deposits in joints. Symptoms include intense pain, swelling, and redness, often affecting the big toe.
| Causes of Gout |
| Dietary Factors: Certain foods rich in purines can trigger gout attacks. |
| Genetic Influences: Family history of gout can increase risk of developing it. |
Risk Factors
Gout attacks often stem from risk factors like obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet high in purines. Elevated uric acid levels in the blood also contribute significantly to the condition.
Lifestyle Choices
Eating foods high in purines can increase the risk of gout. Red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks are common culprits. Alcohol, especially beer, also raises uric acid levels. Being overweight puts extra stress on joints, contributing to gout.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions are linked to gout. High blood pressure and diabetes can increase risk. Kidney disease affects how the body removes uric acid. Family history of gout can also play a role. Some medications might elevate uric acid levels.
Diagnosis
Doctors use medical tests to diagnose gout. Blood tests check uric acid levels. High levels may mean gout. Joint fluid tests are also done. A needle draws fluid from the joint. The fluid is checked for urate crystals. X-rays can show joint damage from gout. These tests help doctors know for sure.
Patients can assess gout at home. They should look for redness and swelling in joints. Pain that starts suddenly is a key sign. Keeping a pain diary helps track symptoms. Noting foods eaten is also important. Certain foods can trigger gout. This information helps doctors with diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Effective treatments for gout attacks include anti-inflammatory medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments. Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial for tailored management and relief.
Medications
Medications are important to treat gout. Doctors often give drugs to reduce pain. Some common drugs are NSAIDs, like ibuprofen. These help to lower swelling. Another medicine used is colchicine. This helps to reduce gout pain. Steroids are also used. These are strong drugs that help a lot. Doctors may give them as pills or shots. Medicines are important to keep gout away. It is best to follow the doctor’s advice.
Natural Remedies
There are many natural remedies for gout. Drinking lots of water helps a lot. Water flushes out bad stuff in the body. Eating cherries can help too. Cherries have special stuff that helps with gout. Some people use ginger and turmeric. These help to lower pain and swelling. Exercise is good too. Moving the body keeps joints healthy. Always check with a doctor before trying new remedies.
Prevention Tips
Gout attacks cause severe joint pain, often in the big toe. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and heat around the affected area. Prevent attacks by staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding high-purine foods.
Dietary Recommendations
Eat more fruits and vegetables. Limit red meat and sugary drinks. Drink plenty of water. Avoid alcohol, especially beer. Opt for low-fat dairy products. Choose whole grains over refined grains. Include nuts and seeds in your diet. Use herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt.
Exercise And Lifestyle
Stay active with regular exercise. Maintain a healthy weight. Avoid sitting for long periods. Stretch your legs often. Choose low-impact activities like walking or swimming. Wear comfortable shoes. Practice good posture. Get enough sleep each night. Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
Living With Gout
Living with Gout can be challenging but Daily Management is key. Support Resources are available to help.
Future Outlook
Scientists are making great strides in understanding gout. New medications are being tested. These could help reduce pain and inflammation. Genetic studies are also underway. They aim to find why some people get gout and others do not.
Researchers are looking for a permanent cure for gout. Some studies focus on diet and lifestyle changes. Others are testing new drugs. Early detection can help manage the disease better. Scientists hope to find more effective treatments soon.
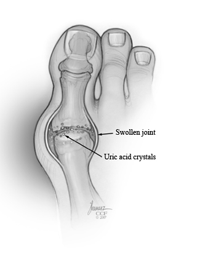
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Symptoms Of A Gout Attack?
A gout attack often presents with sudden, intense joint pain, usually in the big toe. The affected area may be red, swollen, and tender. Pain typically peaks within 24 hours and can last for days to weeks.
How Can I Prevent A Gout Attack?
To prevent a gout attack, maintain a healthy diet low in purines. Stay hydrated, limit alcohol intake, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular exercise can also help manage uric acid levels.
What Triggers A Gout Attack?
Common triggers include high-purine foods like red meat and seafood, excessive alcohol, and sugary drinks. Stress and certain medications can also trigger an attack.
How Is A Gout Attack Treated?
Treatment often involves nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or colchicine. Rest and elevation of the affected joint can help relieve symptoms. Drinking plenty of water can also aid in recovery.
Understanding gout attacks is essential for managing this painful condition. Recognize the symptoms early to seek timely treatment. Lifestyle changes and proper medication can help prevent future attacks. Stay informed and proactive to maintain your health. By doing so, you can significantly reduce the impact of gout on your life.