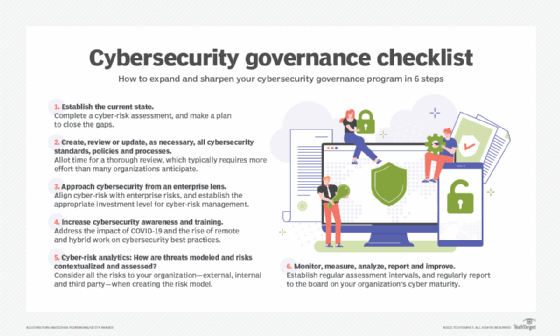
What is Cybersecurity Governance? It may sound like a mouthful, but don’t worry, I’m here to break it down for you. When we talk about cybersecurity governance, we’re basically referring to how organizations and businesses manage and protect their digital assets. It’s like having a set of rules and practices in place to keep the bad guys out and keep our information safe.
Think of it this way: imagine you’re the captain of a ship, and the ship represents your organization. Cybersecurity governance is like having a strong and sturdy helm that steers the ship in the right direction, ensuring it stays on course and avoids any rough waters or pirates that may come it’s way. It’s all about making sure that the organization’s information, systems, and networks are protected from cyber threats.
In this day and age, where everything seems to revolve around technology and the internet, cybersecurity governance is more important than ever.
It’s like having a superpower that can safeguard our confidential data, sensitive information, and even our personal identities. So, let’s dive deeper into the world of cybersecurity governance and learn how it plays a vital role in keeping our digital world safe and secure.
Are you ready? Let’s set sail!
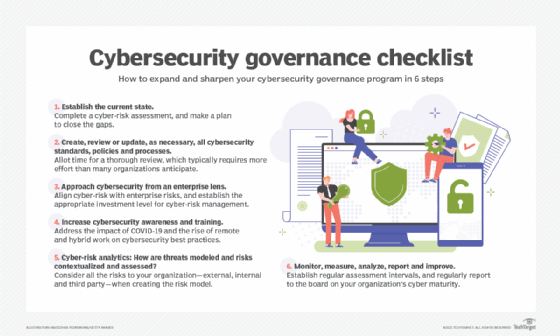
Understanding Cybersecurity Governance: Essential Strategies for Protecting Your Digital Assets
Cybersecurity governance is a critical component of modern business operations and personal online safety. In an increasingly interconnected world, the need for robust cybersecurity measures and effective governance has never been greater.
This article will explore the concept of cybersecurity governance, its importance, and best practices for implementing it in your organization or personal life.
The Basics: What is Cybersecurity Governance?
Cybersecurity governance refers to the policies, processes, and practices put in place to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
It involves the strategic planning, decision-making, and implementation of security controls to protect against cyber threats. Cybersecurity governance encompasses various aspects, including risk management, compliance with applicable laws and regulations, incident response, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation of security measures.
Effective cybersecurity governance involves a combination of technical, organizational, and human-centric strategies. It is essential for organizations of all sizes and across industries to establish and maintain robust governance frameworks to safeguard their sensitive data, networks, and systems from malicious actors.
Key components of cybersecurity governance include:
- Clear policies and procedures: Well-defined and documented security policies and procedures provide a framework for consistent and effective cybersecurity practices.
- Risk assessment and management: Regular assessments of potential threats and vulnerabilities help identify risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Compliance with regulations: Organizations must adhere to relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards to ensure legal and ethical compliance.
- Education and training: Ongoing education and training programs for employees foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and promote responsible digital behaviors.
Cybersecurity Governance for Businesses: Best Practices
For organizations, implementing effective cybersecurity governance is not just about protecting their own assets but also safeguarding the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
Here are some best practices that businesses can follow:
- Establish a cybersecurity governance framework: Develop a comprehensive framework that outlines roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing cybersecurity.
- Assign a dedicated cybersecurity team: Designate a team or individual responsible for overseeing cybersecurity operations and ensuring adherence to governance policies.
- Perform regular risk assessments: Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities and risks through regular assessments to inform decision-making and resource allocation.
- Implement robust security controls: Deploy and maintain a combination of technical controls, such as firewalls and encryption, and non-technical controls, such as incident response plans and employee training.
- Stay up-to-date with emerging threats: Stay informed about the latest cyber threats and vulnerabilities to proactively adapt security measures and respond effectively.
- Maintain incident response capabilities: Establish an incident response plan to effectively address and mitigate the impact of cyber incidents when they occur.
- Regularly evaluate and update security measures: Continuously assess the effectiveness of implemented security controls and update them as needed to stay ahead of evolving threats.
The Role of Individuals in Cybersecurity Governance
Cybersecurity governance is not limited to businesses and organizations alone. Individuals also play a crucial role in protecting their personal digital assets and minimizing cyber risks.
Here are some steps individuals can take:
- Use strong and unique passwords: Create complex passwords and avoid reusing them across multiple platforms.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Enable additional layers of security by using multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Keep software up-to-date: Regularly update operating systems, applications, and devices to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts: Exercise caution when clicking on suspicious links or providing personal information online.
- Backup important data: Regularly backup important files and data to protect against potential data loss due to cyber incidents.
- Educate yourself about cybersecurity: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity best practices and emerging threats to make informed decisions about your digital security.
Future of Cybersecurity Governance
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of cybersecurity governance will also evolve. The increasing reliance on artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and cloud computing presents new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity professionals. To adapt to these changes, continuous learning, collaboration, and innovation will be crucial.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Governance
1. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: The use of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity governance is expected to increase. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies and predict potential threats.
2. Zero Trust Architecture: The concept of zero trust architecture emphasizes that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location or network connection. This approach enhances security by continuously verifying and validating users and devices.
3. Privacy by Design: Privacy considerations will be integrated into cybersecurity governance frameworks from the ground up. Organizations will prioritize data protection and privacy throughout the entire lifecycle of their products and services.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Governance in a Connected World
In an increasingly connected world, the risks and consequences of cyber threats are more significant than ever before.
Cybersecurity governance provides a structured and proactive approach to protect against these threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems.
By implementing effective cybersecurity governance, businesses and individuals can minimize the risks and mitigate the potential damages caused by cyber incidents.
Key Takeaways: What is Cybersecurity Governance?
– Cybersecurity governance refers to the framework and processes put in place to manage and protect an organization’s digital assets from cyber threats.
– It involves the establishment of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
– Effective cybersecurity governance requires a clear understanding of risks, the implementation of security measures, and continuous monitoring and improvement.
– It involves collaboration between different stakeholders, including executives, IT departments, and employees.
– Cybersecurity governance plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of cyberattacks and ensuring the overall security of an organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about cybersecurity governance.
Why is cybersecurity governance important?
Cybersecurity governance is important because it helps organizations protect their sensitive information and systems from cyber threats.
Effective governance ensures that there are clear policies, procedures, and controls in place to manage and mitigate risks. It also helps in complying with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy.
Furthermore, cybersecurity governance helps build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. A robust governance framework demonstrates an organization’s commitment to safeguarding data and, in turn, enhances its reputation as a secure and reliable entity.
What are the key components of cybersecurity governance?
The key components of cybersecurity governance include:
- Leadership and accountability: There should be clear roles and responsibilities for managing cybersecurity at all levels of the organization, with senior leaders taking ultimate accountability.
- Policies and procedures: A comprehensive set of policies and procedures should be developed to guide employees on how to handle and protect data.
- Risk management: Organizations need to identify and assess their cybersecurity risks and put in place controls and measures to mitigate those risks.
- Training and awareness: Regular training and awareness programs should be conducted to educate employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Incident response: A well-defined incident response plan should be in place to effectively manage and respond to cybersecurity incidents.
How does cybersecurity governance differ from cybersecurity management?
Cybersecurity governance and cybersecurity management are closely related but have distinct roles. Cybersecurity governance focuses on establishing a framework of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure the effective management of cybersecurity risks at the organizational level. It is responsible for defining roles, responsibilities, and accountability related to cybersecurity.
On the other hand, cybersecurity management is the implementation and execution of the policies, procedures, and controls set by the governance framework. It involves the day-to-day activities and tasks required to protect organizations from cyber threats, such as patch management, network monitoring, and incident response.
How can organizations assess the effectiveness of their cybersecurity governance?
Organizations can assess the effectiveness of their cybersecurity governance through various methods. One common approach is conducting regular audits and assessments to evaluate compliance with established policies and procedures. This can include internal audits or engaging external auditors or consultants.
Another method is to benchmark cybersecurity practices against recognized frameworks or standards, such as ISO 27001 or NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
These frameworks provide guidelines and best practices for implementing and assessing cybersecurity controls. By comparing their practices against these standards, organizations can identify gaps and areas for improvement in their cybersecurity governance.
What are the benefits of having strong cybersecurity governance?
Having strong cybersecurity governance provides several benefits for organizations:
- Reduced risk: Effective governance helps identify and mitigate cybersecurity risks, reducing the chances of data breaches or cyber-attacks.
- Compliance: Robust governance ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, which helps avoid penalties and reputational damage.
- Business continuity: Cybersecurity governance safeguards critical systems and data, ensuring business operations can continue even in the face of cyber threats.
- Enhanced trust: Strong governance builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, enhancing the organization’s reputation and competitive advantage.
- Cost savings: Proactive governance can save costs associated with data breaches, legal actions, and reputational damage.
Cybersecurity governance is about making sure that organizations protect themselves from cyber threats. It involves creating policies and procedures to keep data safe and using technology to detect and respond to attacks.
Nowadays, cyber threats are becoming more common, so it’s important for companies and individuals to take cybersecurity seriously. Companies need to have a plan in place to prevent cyber-attacks and to respond quickly if an attack does happen.
It’s not enough to just hope that nothing bad will happen – we need to be proactive in protecting our information and systems. By implementing strong cybersecurity governance, we can reduce the risk of cyber-attacks and keep our data safe.