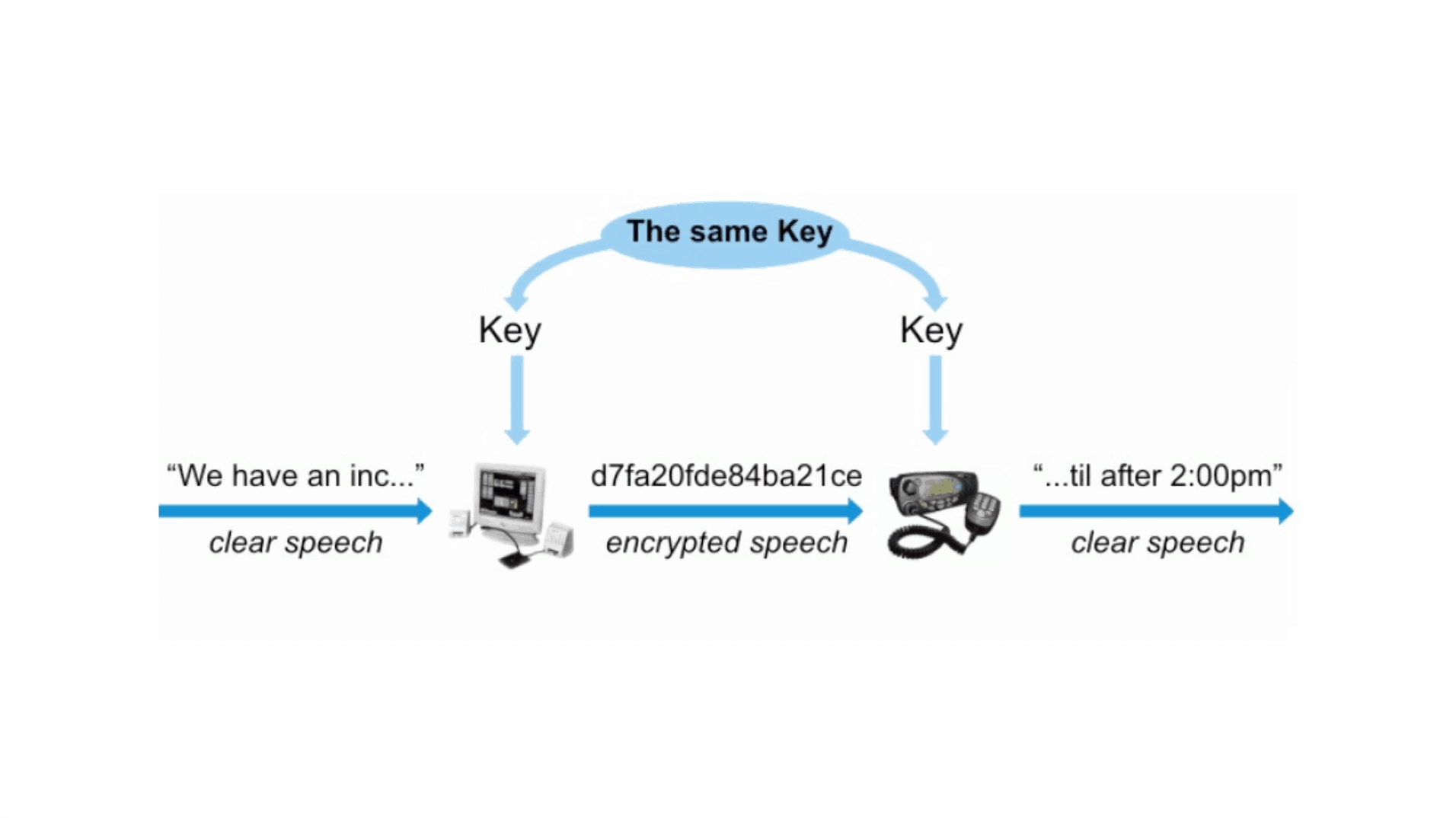
Ever wondered how radio encryption works? Well, let me break it down for you in a way that’s easy to understand. Radio encryption is like a secret code that protects the messages being transmitted over the airwaves.
It adds a layer of security to ensure that only authorized parties can access and understand the information. So, how does this fascinating technology actually work?
Let’s dive in and find out!
Encryption is like putting your message in a locked box and only giving the key to the intended recipient. In the world of radio, this involves using complex algorithms that scramble the original message into an unintelligible jumble of data.
Without the correct encryption key, it becomes nearly impossible to decipher the true meaning of the message. It’s like trying to solve a puzzle without the right pieces.
Radio encryption systems use a combination of mathematical algorithms and unique keys to encrypt and decrypt messages. These algorithms are designed to make it extremely difficult for anyone without the authorized key to decrypt the message.
It’s like having a secret language that only those with the secret knowledge can understand. This ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure.
So, the next time you listen to the radio, whether it’s your favorite music station or emergency broadcasts, remember that behind the scenes, radio encryption is working tirelessly to protect the messages being transmitted.
It’s a fascinating technology that keeps information safe and sound, ensuring that only the intended recipients can unlock its secrets. Now that you know a little more about radio encryption, let’s explore it in more detail and uncover its inner workings. Let’s dive deeper together!
In the world of radio communication, encryption is used to secure sensitive information from unauthorized access.
While the specific workings may vary depending on the system being used, radio encryption generally involves converting the original message into a coded format using an encryption algorithm.
This algorithm ensures that only authorized recipients with the corresponding decryption key can decode and understand the message. By employing radio encryption, organizations can safeguard their communications and maintain confidentiality.

How Does Radio Encryption Work?
Radio encryption is a crucial technology that enables secure communication over radio waves. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of how radio encryption works, its benefits, and its applications in various industries.
From the basics of encryption to the advanced algorithms used in modern systems, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of radio encryption.
1. The Basics of Radio Encryption
Radio encryption is a method of encoding information transmitted through radio waves to make it secure and unintelligible to unauthorized listeners.
It involves the use of cryptographic algorithms to convert plain text into ciphertext, which can only be decrypted by authorized users possessing the corresponding decryption key. Encryption ensures that even if intercepted, the information remains confidential.
Encryption algorithms used in radio encryption systems typically employ mathematical operations and complex algorithms to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the transmitted data.
These algorithms are designed to make it computationally infeasible for an attacker to reverse-engineer the encryption process without the decryption key.
Types of Encryption Algorithms
There are several types of encryption algorithms used in radio encryption systems, including symmetric key encryption and asymmetric key encryption. Symmetric key encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric key encryption involves the use of a public-private key pair.
Symmetric key encryption algorithms, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Data Encryption Standard (DES), are faster and more efficient for encrypting and decrypting large amounts of data.
Asymmetric key encryption algorithms, such as RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), provide a higher level of security but are slower due to the complexity of the mathematical operations involved.
2. Advantages of Radio Encryption
Radio encryption offers numerous advantages in terms of secure communication, data protection, and privacy. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that only authorized parties can access and understand the transmitted information, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized interception.
2. Authentication: Radio encryption can verify the authenticity of the sender and receiver, preventing unauthorized users from masquerading as legitimate parties.
3. Data Integrity: Encryption algorithms can detect any alterations or tampering with the data during transmission, ensuring the integrity of the information.
4. Compliance with Regulations: Many industries, such as government agencies and defense organizations, have strict regulations that require the use of radio encryption to safeguard sensitive information.
5. Prevention of Eavesdropping: Encryption makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized listeners to decrypt and understand the intercepted radio transmissions, preventing valuable information from falling into the wrong hands.
Applications of Radio Encryption
Radio encryption finds applications in various industries, including:
1. Military and Defense: Secure communication is crucial in military operations to protect classified information and enable secure command and control.
2. Law Enforcement: Police departments and other law enforcement agencies use radio encryption to prevent criminals from intercepting their communications and gathering sensitive information.
3. Emergency Services: Fire departments, ambulance services, and other emergency response organizations rely on radio encryption to protect sensitive operational information and ensure secure communication during critical situations.
4. Aviation: Air traffic controllers, pilots, and airports use radio encryption to ensure secure communication and prevent unauthorized transmissions that may pose risks to flight safety.
5. Private Security: Private security firms employ radio encryption to protect communication between their personnel, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
3. Encryption Algorithms in Modern Radio Systems
Modern radio encryption systems utilize advanced encryption algorithms and protocols to provide robust security and combat evolving threats.
These algorithms focus on key exchange, authentication, and data confidentiality to create secure communication channels. Some of the commonly used encryption algorithms in modern radio systems include:
1. P25 Encryption: Project 25 (P25) is a suite of standards for digital radio communications used by public safety organizations. P25 encryption employs Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to ensure secure communication.
2. Tetra Encryption: Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA) is a digital trunked radio standard used by various organizations, including emergency services. TETRA encryption utilizes various algorithms such as TEA, Kasumi, and AES.
3. DES-OFB: Data Encryption Standard with Output Feedback (DES-OFB) is a symmetric key encryption algorithm used in legacy systems. It encrypts data in blocks and is primarily used for backward compatibility.
4. AES: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a widely used symmetric key encryption algorithm that provides secure and efficient encryption for sensitive information. It is favored for its robust security and high performance.
5. RSA: Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) is an asymmetric key encryption algorithm widely used for secure key exchange and digital signatures. It is based on the mathematical complexity of factoring large prime numbers.
Radio encryption is an essential technology that ensures secure communication by converting data into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms.
It provides confidentiality, authentication, and data integrity, making it vital in industries such as the military, emergency services, and aviation.
Various encryption algorithms, both symmetric and asymmetric, are used in modern radio systems to ensure robust security and combat evolving threats.
Understanding how radio encryption works helps us appreciate its importance in our increasingly interconnected and information-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are you curious about how radio encryption works? Look no further! We’ve got answers to all your burning questions right here.
Q: Can anyone listen to encrypted radio communications?
A: No, encrypted radio communications cannot be easily intercepted and understood by unauthorized individuals. Encryption involves encoding the information transmitted over the radio waves so that it can only be deciphered by authorized recipients who possess the necessary decryption keys or codes. This ensures that the communication remains secure and confidential.
Encryption algorithms use complex mathematical calculations to convert the original voice or data signals into an encrypted form. This process makes the information unintelligible to anyone who doesn’t have the correct decryption key.
As a result, even if someone were to intercept the encrypted radio transmission, they would not be able to make sense of the message without the proper decryption tools. This is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive information shared over radio channels, such as law enforcement operations or military communications.
Q: How do encryption keys work in radio communication?
A: Encryption keys play a central role in radio communication encryption. An encryption key is a unique piece of information that is used to encrypt and decrypt data.
In the context of radio encryption, these keys are typically created and managed by a central authority, such as a government agency or an organization responsible for managing the radio communication system.
When a sender wishes to transmit an encrypted message, they first obtain the appropriate encryption key from the central authority. The encryption algorithm then uses this key to convert the original message into an encrypted form.
At the receiving end, the authorized recipient uses the corresponding decryption key to reverse the encryption process and retrieve the original message. The encryption keys are kept secret and are known only to the parties involved to ensure the security of the communication.
Q: What are the benefits of using radio encryption?
A: Radio encryption offers several benefits in the realm of communication security. The primary advantage is the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access.
By encrypting radio communications, only those with the proper decryption keys can understand and access the transmitted message. This prevents malicious actors from intercepting and exploiting the information.
Another benefit is the assurance of message integrity. Encryption algorithms often include mechanisms to detect any tampering or alteration of the encrypted message during transmission.
These mechanisms help ensure that the received message has not been modified or tampered with en route. This helps build trust and confidence in the integrity of the communication.
Q: Can radio encryption be broken?
A: While no encryption is completely unbreakable, modern encryption techniques used in radio communications are highly secure. They employ sophisticated algorithms and use long encryption keys to make the task of encryption breaking extremely difficult and time-consuming.
Breaking radio encryption would require significant computational power, advanced technical skills, and a substantial amount of time. Additionally, encryption systems are constantly being updated and improved to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities.
This continuous evolution ensures that the encryption remains robust and resilient against attacks. However, it is important to regularly update encryption systems and protocols to maintain their effectiveness over time.
Q: Are there different types of radio encryption?
A: Yes, there are multiple types of radio encryption used in various communications systems. The choice of encryption method depends on factors such as the level of security required, the specific radio communication system being used, and the regulatory or legal requirements in place.
Some commonly used encryption systems include DES (Data Encryption Standard), AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), and P25 (Project 25).
Each of these encryption methods employs different algorithms and encryption keys to secure radio communications. The selection of a particular encryption scheme is based on the needs and specifications of the organization or agency utilizing the radio communication system.
Understanding how radio encryption works is important for keeping communications secure and private. Encryption is like putting a secret code on messages, so only the right people can understand them.
It uses a special key to scramble the information, making it unreadable to anyone without the key. This ensures that sensitive information, like military or emergency communications, stays protected from unauthorized access.
Radio encryption is a crucial tool in maintaining security and confidentiality in various industries and organizations.