What happens when you reset encrypted data? Well, it’s an intriguing question, isn’t it? Imagine having a magic button that could reset all your encrypted data in an instant. What would happen? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of encrypted data and find out!
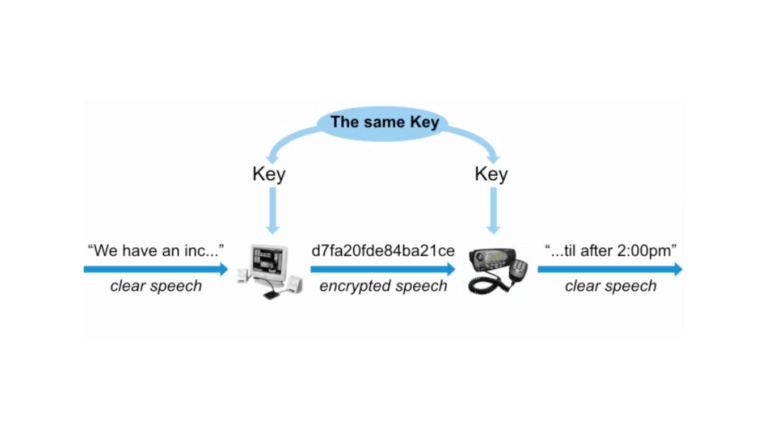
We all know that data can be sensitive and valuable, and that’s why encryption comes into play. Encryption is like turning your data into a secret code that only you can decipher. It keeps your information secure and out of the wrong hands. But what happens when you hit the reset button on encrypted data?
Resetting encrypted data is like erasing the secret code that protected it. It’s like having amnesia and forgetting the password to a locked box. Suddenly, the once-secure data becomes inaccessible and unreadable. But fear not, my young curious minds! There’s more to this story, and we’re about to explore it together.
What Happens When You Reset Encrypted Data?
Resetting encrypted data can have significant consequences, both positive and negative. It’s essential to understand the implications before taking such action. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of resetting encrypted data and its potential outcomes. From the process itself to the impact on data security, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions. So, let’s dive into the world of resetting encrypted data and discover what happens when you take this step.
The Resetting Process: How Encrypted Data is Reset
When you reset encrypted data, the process typically involves reverting the data back to its original, unencrypted state. This can be achieved by decrypting the data, which essentially removes the encryption algorithm or key that was used to protect it. The exact method may vary depending on the encryption system in place.
Resetting encrypted data usually requires authentication from the authorized user or administrator. This is to ensure that only authorized individuals have the power to reset the data and prevent unauthorized access. The authentication process may involve verifying credentials, such as passwords or biometric information, to ensure the integrity and security of the reset action.
It’s important to note that resetting encrypted data should be approached with caution. The process often results in the permanent loss of the encryption keys or metadata associated with the encrypted data. This means that once reset, the data may no longer be recoverable in its encrypted form.
Data Security Implications of Resetting Encrypted Data
The decision to reset encrypted data can have significant implications for data security. On one hand, it may provide an opportunity to regain access to data that was otherwise inaccessible due to lost or forgotten encryption keys. This can be beneficial in situations where access to the data is crucial for business operations or legal compliance.
On the other hand, resetting encrypted data can also pose risks to data security. By resetting the encryption, you effectively remove the protective layer that safeguards the data from unauthorized access. This means that if the reset data is not adequately secured with new encryption measures, it becomes vulnerable to potential breaches.
It is essential to carefully evaluate the potential risks and benefits before resetting encrypted data. Consider factors such as the sensitivity of the data, the need for access, and the feasibility of implementing alternative security measures. Consulting with experts in data security can provide valuable insights into the best course of action.
Benefits of Resetting Encrypted Data
1. Regaining Access: One of the primary benefits of resetting encrypted data is the ability to regain access to previously inaccessible data. This can be crucial in situations where important information or files are locked due to lost encryption keys or forgotten passwords.
2. Simplified Management: Resetting encrypted data can simplify data management processes by removing the complexities associated with encryption. It eliminates the need for managing and storing encryption keys, simplifying the overall data security infrastructure.
3. Compliance and Legal Requirements: In some cases, resetting encrypted data may be necessary to meet compliance and legal requirements. By decrypting the data, organizations can ensure that they have proper access to the required information during audits or legal proceedings.
Drawbacks and Risks of Resetting Encrypted Data
1. Data Vulnerability: Resetting encrypted data without implementing alternative security measures can leave the data vulnerable to unauthorized access and potential breaches. It is crucial to ensure that appropriate security measures are in place before proceeding with resetting the data.
2. Loss of Encryption: When encrypted data is reset, the encryption algorithm or key used to protect the data is removed. This means that if the data is not properly secured with new encryption methods, it becomes more susceptible to unauthorized access.
3. Permanent Loss of Encrypted Data: Resetting encrypted data often results in the permanent loss of the encryption keys or metadata associated with the data. This means that the data may no longer be recoverable in its encrypted form, which can be a significant drawback.
Best Practices for Resetting Encrypted Data
1. Backup Data: Before resetting encrypted data, it is essential to create backups of all critical information. This ensures that even if data is lost during the reset process, you have a copy available for recovery.
2. Implement New Security Measures: After resetting encrypted data, it is crucial to establish new security measures to protect the data from unauthorized access. This includes implementing robust encryption methods, access controls, and regular security audits.
3. Seek Expert Advice: If you are unsure about the implications of resetting encrypted data, it’s advisable to seek expert advice. Data security professionals can provide guidance specific to your situation and help you make informed decisions.
Post-Resetting Actions: Ensuring Data Protection and Security
After resetting encrypted data, it’s essential to take additional steps to ensure data protection and security. Here are three key actions to consider:
1. Encryption Key Management
Proper encryption key management is critical to maintaining data security post-reset. Establish a robust system for generating, storing, and managing encryption keys. Make sure to regularly update and rotate keys to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Add an extra layer of security by implementing multi-factor authentication. Require users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a fingerprint scan, to access sensitive data. This helps prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining unauthorized access even if encryption is compromised.
3. Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities in your system. This includes regular reviews of access controls, encryption protocols, and security measures. Stay up-to-date with the latest industry standards and best practices to ensure optimal data protection.
Resetting Encrypted Data: A Balancing Act
Resetting encrypted data offers both benefits and risks, making it a balancing act for organizations and individuals. It’s crucial to understand the implications and weigh the potential benefits against the risks before taking this step. By following best practices and seeking expert advice, you can minimize security risks and ensure the protection of your data.
Key Takeaways: What Happens When You Reset Encrypted Data?
- Resetting encrypted data erases all the stored information and makes it unreadable.
- When you reset encrypted data, it is impossible to recover the original information without the decryption key.
- Resetting encrypted data ensures that the data is no longer accessible to unauthorized individuals.
- After resetting encrypted data, it is necessary to re-encrypt the information to maintain its security.
- Resetting encrypted data is a precautionary measure to protect sensitive information from being compromised.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section where we answer your questions about resetting encrypted data. Whether you’re curious about the process or concerned about the consequences, we’ve got you covered. Read on to find out everything you need to know.
1. Is resetting encrypted data the same as deleting it?
No, resetting encrypted data is not the same as deleting it. When you reset encrypted data, you are essentially returning it to its original encrypted state. The encryption algorithm ensures that the data remains secure, even after resetting. On the other hand, deleting encrypted data permanently removes it from the system, making it unrecoverable.
Resetting encrypted data is often done to clean up and organize your files while maintaining the security of the data. It is a useful technique when you want to remove unnecessary data without compromising sensitive information.
2. Can I recover reset encrypted data?
No, once encrypted data is reset, it cannot be recovered unless you have a backup of the original encrypted file. The purpose of encryption is to protect the data from unauthorized access and tampering. Resetting the data essentially reverts it back to its original encrypted state, rendering it inaccessible without proper decryption.
It is crucial to have backups of your encrypted data before resetting it to avoid permanent loss. Regular backups ensure that if any data is accidentally reset or lost, you can restore it from a previous backup with minimal disruption to your workflow.
3. Will resetting encrypted data affect other files on my system?
No, resetting encrypted data does not affect other files on your system. The reset process only applies to the specific encrypted files you choose to reset. Other files, whether encrypted or not, remain untouched and unaffected.
It’s important to note that resetting encrypted data only modifies the encryption status of the selected files. It does not have any impact on the rest of your system or other unrelated data.
4. What precautions should I take before resetting encrypted data?
Before resetting encrypted data, it’s crucial to have a backup of the files you plan to reset. This ensures that in case of accidental loss or the need for the data in the future, you have a copy readily available. Additionally, double-check that you are resetting the correct files to avoid any unintended consequences.
Another precaution to consider is verifying that you have the necessary decryption keys or passwords to access the reset data, should you need it at a later time. Losing access to the decryption keys can result in permanent loss of the data, so always keep them securely stored.
5. Are there any risks involved in resetting encrypted data?
There are minimal risks involved in resetting encrypted data when done correctly. As long as you have backups and take appropriate measures such as verifying the files and ensuring you have the necessary decryption keys, you can safely reset encrypted data without significant risks.
However, it’s essential to be cautious when resetting encrypted data, as any unintentional mistakes during the process can lead to permanent loss or make the data irretrievable. It’s always recommended to double-check and have a clear understanding of the consequences before proceeding.
Summary
Hey there! So, let’s wrap up what we learned about resetting encrypted data. When you reset encrypted data, it doesn’t magically disappear. Instead, the encryption key gets deleted, making the data really hard to access. But here’s the thing, even though it’s difficult, it’s not impossible for skilled hackers to still get their hands on it. So, be careful!
In a nutshell, resetting encrypted data is like throwing away the key to a locked box. The box is there, but without the key, it’s tough to open. Just keep in mind that even without the key, determined people can still find a way in. So, stay cautious and protect your important info with strong encryption!