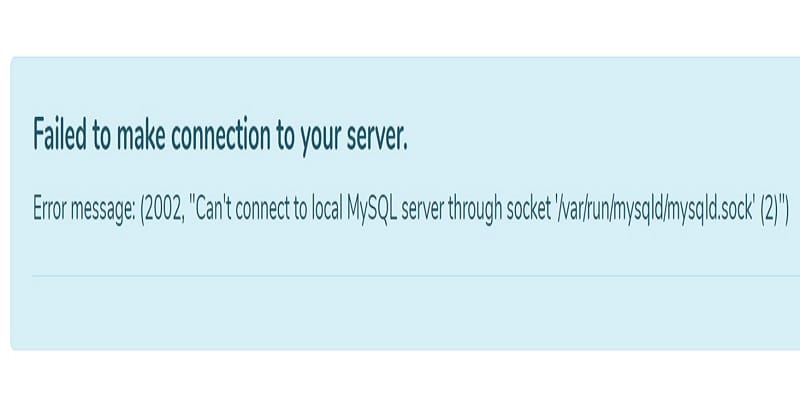
The “Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock'” error is a common roadblock that many MySQL users encounter. This error can disrupt your database operations and needs immediate attention. This article provides a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot and resolve this error effectively.
Decoding the Issue: What “Can’t Connect to Local MySQL Server Through Socket” Really Means
Before diving into the solutions, it’s crucial to understand what this error message signifies. The error occurs when a MySQL client application tries to connect to the MySQL server but fails. The UNIX socket, usually located at /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock, serves as the communication endpoint between the MySQL server and client applications. If this connection fails, you’ll encounter the error.
Root Causes: Unveiling the Reasons Behind the Error
There are several reasons why this error might occur:
- MySQL Server Not Running: If the MySQL service is not running, the socket file won’t be created, leading to the error.
- Incorrect File Path: Sometimes, the path to the
mysqld.sockfile in the MySQL configuration may be incorrect. - Permission Issues: Inadequate permissions can prevent the MySQL client from accessing the
mysqld.sockfile. - Firewall Restrictions: Network firewalls can sometimes block the necessary ports, causing this error.
A Practical Guide: Troubleshooting Steps for “Can’t Connect to Local MySQL Server Through Socket”
Step 1: Check if MySQL Server is Running
Open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo systemctl status mysql
If the server is not running, start it with:
sudo systemctl start mysql
Step 2: Verify the Existence of mysqld.sock File
Check if the mysqld.sock file exists in the /var/run/mysqld/ directory:
ls /var/run/mysqld/
Step 3: Check File and Directory Permissions
Run the following command to check the permissions:
ls -la /var/run/mysqld/
If the permissions are incorrect, modify them using the chmod and chown commands.
Step 4: Validate MySQL Configuration File
Open the MySQL configuration file (my.cnf) and look for the line specifying the socket file. Make sure it points to /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock.
Step 5: Restart MySQL Service
After making any changes, always restart the MySQL service:
sudo systemctl restart mysql
Expert Insights: Advanced Solutions for Resolving the Error
Using Netstat to Verify Port Status
Use the netstat command to check if MySQL’s default port (3306) is open:
netstat -an | grep 3306
Check System Logs
System logs can provide additional clues. Use the tail command to view the latest entries in the MySQL error log:
tail -f /var/log/mysql/error.log
Final Takeaways: How to Prevent the Error in the Future:
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on the MySQL service status.
- Backup Configuration Files: Before making changes to any configuration files, always take backups.
- Set Proper Permissions: Ensure that the
mysqld.sockfile and its directory have the correct permissions.
The “Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock'” error can be a stumbling block, but it’s usually straightforward to resolve. By following this step-by-step guide, you should be able to troubleshoot and fix the issue effectively. Happy database managing!