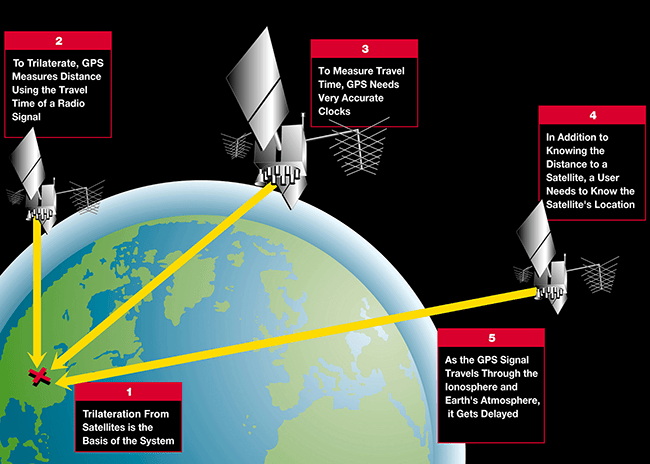
Do you ever wonder how your smartphone knows your exact location when you’re using navigation apps or searching for nearby restaurants?
It’s all possible thanks to a technology called Wi-Fi positioning. But you might be wondering, “How does Wi-Fi positioning contribute to geolocation?” Well, get ready to dive into the fascinating world of location-based services and discover how Wi-Fi plays a vital role in determining your whereabouts.
You see, Wi-Fi positioning leverages the signals emitted by Wi-Fi access points to estimate a device’s location. It’s like a digital treasure hunt where your smartphone uses these signals as clues to pinpoint where you are. And the best part? Wi-Fi is practically everywhere nowadays, making it a powerful tool for geolocation.
So, how does it work exactly? Imagine you’re in a shopping mall. As you move through the mall, your smartphone continuously scans for nearby Wi-Fi networks.
It detects multiple access points and notes their signal strengths. By comparing this information with a vast database of Wi-Fi networks and their known locations, your device can accurately determine where you are within the mall. It’s like having your own personal GPS but with Wi-Fi as the guiding star. Fascinating, isn’t it?
Now that you have a glimpse into the magic of Wi-Fi positioning, let’s explore its practical applications and how it enhances our daily lives.
Get ready to uncover the ways in which this technology empowers navigation apps, indoor mapping, geo-targeted advertising, and much more. So, buckle up, and let’s embark on this exciting journey where Wi-Fi and geolocation intersect!
Wi-Fi positioning plays a significant role in geolocation by utilizing the signals emitted by Wi-Fi networks. Through triangulation and signal strength analysis, Wi-Fi positioning helps determine the location of a device. This information is then used in various applications, such as mapping services and location-based marketing. By combining Wi-Fi signals with GPS and cellular data, geolocation accuracy is greatly enhanced, allowing for precise tracking and navigation. This technology enables a wide range of services that rely on accurate location information for both individuals and businesses.
How Does Wi-fi Positioning Contribute to Geolocation?
Welcome to this in-depth exploration of how Wi-fi positioning contributes to geolocation. In our increasingly connected world, geolocation has become an integral part of many applications and services.
Whether it’s finding your way with GPS or discovering nearby attractions, understanding how Wi-fi positioning enhances geolocation is crucial.
In this article, we will dive into the technical aspects of Wi-fi positioning and its impact on geolocation accuracy, as well as explore the benefits, challenges, and future of this technology.
Basics of Wi-fi Positioning
Wi-fi positioning is a technique used to determine the geographical location of a person or device by utilizing Wi-fi signals. It works by analyzing the strength and quality of Wi-Fi signals from nearby access points to estimate the device’s position.
Unlike GPS, which relies on satellite signals, Wi-fi positioning takes advantage of existing Wi-fi infrastructure, making it widely available and cost-effective.
When a device wants to determine its location, it scans for nearby Wi-fi access points and measures the signal strength of each.
By comparing these measurements with a database of known Wi-fi access point locations, the device can triangulate its position. This approach allows for relatively accurate geolocation, especially in urban areas with dense Wi-fi coverage.
One of the key benefits of Wi-fi positioning is its versatility. Unlike GPS, which struggles with accuracy indoors or in urban canyons, Wi-fi signals can penetrate buildings and provide reliable positioning data. This makes it ideal for location-based services in airports, shopping malls, and even underground transportation networks.
The Role of Signal Strength in Wi-fi Positioning
Signal strength is a critical factor in Wi-fi positioning. As a device moves closer to a Wi-fi access point, the signal strength increases, and vice versa. By measuring this strength, the device can estimate its distance from the access point. However, signal strength alone is not enough to determine position accurately.
Other factors, such as obstacles, interference, and multi-path effects, can affect signal strength and introduce errors in positioning. For example, walls, furniture, and even people can attenuate Wi-fi signals, leading to inaccuracies in distance estimation.
Additionally, interference from neighboring Wi-fi networks or electronic devices can further impact signal quality, leading to potential positioning errors.
To mitigate these challenges, Wi-fi positioning algorithms take into account not only signal strength but also factors like signal quality, access point density, and the presence of obstacles.
These algorithms use machine learning and statistical techniques to model the relationship between signal characteristics and location. As a result, they can improve the accuracy and reliability of Wi-fi positioning systems.
Benefits of Wi-fi Positioning
Wi-fi positioning offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for geolocation applications:
- Indoor Accuracy: Unlike GPS, Wi-fi positioning excels at providing accurate location data indoors, where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable. This makes it a valuable tool for indoor navigation and location-based services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Wi-fi positioning leverages existing Wi-fi infrastructure, eliminating the need for additional hardware investments. This makes it a cost-effective solution for businesses and service providers.
- Ubiquitous Coverage: Wi-fi networks are widespread in urban areas, providing extensive coverage for geolocation applications. Users can rely on Wi-fi positioning even in densely populated areas.
- Seamless Integration: Wi-fi positioning can be seamlessly integrated into existing applications and services, thanks to its compatibility with standard Wi-fi protocols. This allows developers to leverage Wi-fi positioning without significant modifications to their codebase.
With these benefits, Wi-fi positioning has become a fundamental component of various geolocation applications, including mapping services, asset tracking, and location-based advertising.
Challenges and Future of Wi-fi Positioning
While Wi-fi positioning offers many advantages, it also faces certain challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance:
- Data Accuracy: Wi-fi positioning relies on accurate Wi-fi access point location databases. Outdated or incorrect data can lead to positioning errors. Maintaining and updating these databases is crucial to ensure accurate geolocation.
- Data Privacy: Wi-fi positioning involves collecting and analyzing Wi-fi signals, potentially raising privacy concerns. To address these concerns, strict data protection measures and encryption protocols must be implemented.
- Interference and Obstructions: Signal interference from neighboring Wi-fi networks or physical obstructions can impact positioning accuracy. Advanced signal processing techniques and improved hardware can help mitigate these challenges.
The future of Wi-fi positioning lies in further advancements in machine learning algorithms, improved hardware capabilities, and the integration of other positioning technologies.
Combining Wi-fi with other technologies like GPS, Bluetooth, or cellular networks can enhance geolocation accuracy and reliability.
Additionally, the emergence of 5G networks and the deployment of more Wi-fi access points will create new opportunities for precise and seamless positioning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wi-Fi positioning is a technology that uses wireless signals from Wi-Fi networks to determine the location of a device or user. This technology has various applications, including geolocation. Let’s explore some common questions related to how Wi-Fi positioning contributes to geolocation.
1. How does Wi-Fi positioning work to determine geolocation?
Wi-Fi positioning relies on the principle that Wi-Fi signals can be received at different strengths depending on how close a device is to a Wi-Fi access point.
By measuring signal strength from multiple access points, a device can compare the received power levels and determine its location in relation to those access points. This information can then be used to provide geolocation data.
Wi-Fi positioning can use techniques like triangulation or fingerprinting to improve location accuracy. Triangulation involves measuring the signal strength from at least three access points and calculating the device’s position based on the intersecting signal ranges.
Fingerprinting, on the other hand, involves creating a database of signal patterns from different locations and comparing the received signal pattern to identify the device’s location.
2. What are the advantages of using Wi-Fi positioning for geolocation?
Wi-Fi positioning offers several advantages when it comes to geolocation. Firstly, Wi-Fi signals are widely available in many areas, making it possible to determine the location of devices in a broad range of environments. Wi-Fi is commonly found in public spaces, businesses, and even residential areas, increasing the coverage for geolocation.
Additionally, Wi-Fi can provide indoor positioning capabilities, where GPS signals may be weaker or unavailable. This is particularly useful for applications like indoor navigation in malls, airports, or museums.
Wi-Fi positioning can complement GPS to provide more accurate and reliable geolocation data, especially in urban environments with tall buildings or obstructed satellite signals.
3. Is Wi-Fi positioning accurate for geolocation purposes?
Wi-Fi positioning can provide reasonably accurate geolocation data, although the level of accuracy can vary depending on factors like the density of Wi-Fi access points, signal interference, and the quality of the positioning algorithms used. In urban areas with a high density of access points, the accuracy can be within a few meters.
However, in some cases, the accuracy may be lower, especially in rural or remote areas with fewer access points. It’s important to note that Wi-Fi positioning is not as accurate as GPS for outdoor environments. It’s best suited for applications where moderate accuracy is sufficient, such as location-based services or asset tracking within buildings.
4. Are there any privacy concerns with Wi-Fi positioning for geolocation?
There can be privacy concerns with Wi-Fi positioning, as it involves collecting and processing data about the locations of devices. It’s crucial for service providers and app developers to handle this data responsibly, ensuring that it is anonymized and protected from unauthorized access.
Among the privacy measures, Wi-Fi positioning systems often use techniques like MAC address anonymization or encryption to safeguard user privacy.
MAC address randomization can prevent the device’s unique identifier from being linked to its geolocation data, enhancing anonymity.
5. How is Wi-Fi positioning different from GPS for geolocation?
While both Wi-Fi positioning and GPS are used for geolocation, they rely on different technologies. GPS uses signals from satellites to determine the location of a device, which is highly accurate outdoors but can be limited by obstructions like buildings or trees.
Wi-Fi positioning, on the other hand, relies on signals from Wi-Fi access points and can provide accurate geolocation indoors or in urban environments where GPS signals may be weak. Moreover, Wi-Fi positioning can also complement GPS by providing backup or secondary geolocation data in case of GPS signal loss.
So, to wrap things up, Wi-Fi positioning helps us figure out where we are. It looks at the signals from Wi-Fi routers to determine our location. This is useful for lots of things, like finding the nearest coffee shop or getting directions to a new place.
But Wi-Fi positioning isn’t perfect. Sometimes the signals can be weak or blocked, which can affect the accuracy. And there are privacy concerns too, as our location data can be tracked. So while Wi-Fi positioning is helpful, we need to be aware of its limitations and use it responsibly.