What is Spot Welding? Let me introduce you to this fascinating process that joins two metal surfaces together with a powerful burst of heat.
Have you ever wondered how cars, appliances, or even ships are constructed? Well, spot welding plays a crucial role in their assembly, and I’m here to give you the lowdown on this amazing technique.
Spot welding, my friend, is like the superhero of the welding world. It’s quick, efficient, and can create incredibly strong bonds between metal sheets.
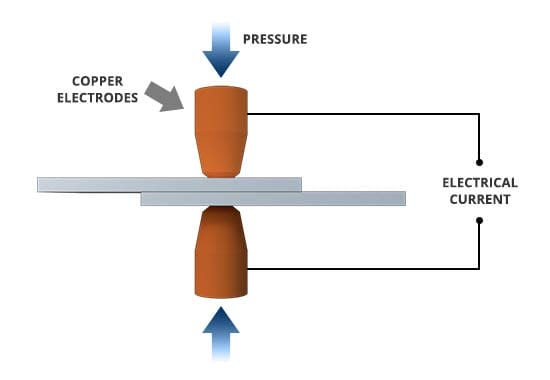
Picture this: two metal surfaces come together, and a pair of copper electrodes apply pressure while sending an electric current through them. The result? The metal surfaces heat up and melt, fusing together into a solid connection in just a matter of seconds.
Now, you may be wondering when and where spot welding is used. Well, it’s all around us! Spot welding is widely used in the automotive industry to assemble car bodies and frames.
It also finds its place in manufacturing appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, where it helps create sturdy and durable structures. So, the next time you spot a car or a household appliance, remember that spot welding played a vital role in bringing it to life!
What is Spot Welding? An Introduction to a Joining Technique
Spot welding is a process commonly used in manufacturing to join two metal surfaces together. It involves applying pressure and heat to create a weld in a localized area.
This type of welding is known for its speed and efficiency, making it a popular choice in industries such as automotive and aerospace. Spot welding is durable and produces a strong bond, making it ideal for connecting thin sheets of metal. Overall, it’s a versatile and reliable method for joining metals together.
Understanding Spot Welding: The Process and Equipment
Spot welding is a form of resistance welding, which means it utilizes the resistance generated by electric current passing through the materials being joined. The process involves three main components: the two metal workpieces to be welded, the electrode tips that deliver the energy to the workpieces, and the power supply that produces the necessary current and controls the welding parameters.
During spot welding, the two metal surfaces are clamped together between the electrode tips. When the electric current flows through the workpieces, a localized heat is generated at the interface, causing the metals to melt and form a weld nugget.
The pressure applied by the electrodes ensures good contact and enables the fusion of the metals. Once the energy is removed, the weld solidifies, creating a strong, durable bond.
Benefits of Spot Welding
Spot welding offers numerous advantages compared to other welding techniques. First and foremost, it is highly efficient and can be performed quickly, making it ideal for mass production.
Its automation capability allows for increased productivity and consistency in terms of weld quality and appearance. Additionally, spot welding produces a clean and precise joint, without the need for external filler materials, reducing overall production costs. The spot welds are also aesthetically appealing, with minimal scarring or excess material.
Spot welding is especially suitable for joining thin metal sheets, as it minimizes thermal distortion and leaves no visible marks on the opposite side.
The process is versatile and can be applied to a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Furthermore, spot welding allows for easy disassembly and rework, as the welded parts can be separated without damaging the materials.
Applications of Spot Welding in Various Industries
Spot welding finds extensive applications across different industries, showcasing its versatility and reliability. In the automotive industry, spot welding is heavily used for the manufacturing of car bodies, joining various metal components to ensure structural integrity.
The aerospace sector utilizes spot welding for aircraft assembly, connecting aluminum or titanium sheets used in fuselages, wings, and engine structures.
Electronics manufacturers also benefit from spot welding, using the technique to join electrical components together. It ensures consistent electrical conductivity and helps prevent corrosion or damage due to loosely connected parts.
Spot welding is also commonly employed in the production of household appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, where it facilitates the assembly of metal casings and internal components.
Tips for Successful Spot Welding
To achieve optimal weld quality and consistent results, following certain tips can greatly enhance the spot welding process. Firstly, selecting the appropriate electrode material and shape is crucial. Copper alloys are commonly used due to their excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance. The electrode shape should match the joint configuration, providing sufficient contact area.
Maintaining clean work surfaces is essential for successful spot welding. Grease, dirt, or oxide layers can hinder proper current flow and lead to weak welds.
Therefore, it is vital to remove any contaminants before the welding process. Additionally, proper control of welding parameters, such as current intensity, electrode force, and welding time, is necessary to achieve desired weld characteristics.
Monitoring and inspecting weld quality is crucial for ensuring the reliability and durability of spot welds. Visual inspections, non-destructive testing methods, and strength testing can be employed to detect any defects or inconsistencies. Regular maintenance and calibration of spot welding equipment is also necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Spot Welding Techniques and Variations
Resistance Spot Welding vs. Projection Spot Welding: A Comparison
Resistance spot welding and projection spot welding are two commonly used variations of spot welding. While both techniques utilize the same principle of localized heat generation, they differ in their applications and specific processes.
Resistance spot welding involves welding thin metal sheets or components together, where the electrode tips directly contact the workpieces.
It is suitable for joining materials with thicknesses ranging from 0.5mm to 6mm. Projection spot welding, on the other hand, is utilized when additional strength or reinforcing spots are required. It involves the use of specially designed projections on one of the workpieces, creating localized areas of higher current concentration and temperature during welding.
Benefits of Resistance Spot Welding
Resistance spot welding offers several advantages over other welding techniques. The process is fast, efficient, and requires minimal heat input, making it suitable for high-volume production. It produces consistent and reliable welds, with excellent strength and electrical conductivity.
Resistance spot welding also allows for precise control of weld parameters, ensuring consistent quality throughout the welding process.
Factors Affecting Spot Weld Quality
Several factors can impact the quality and integrity of spot welds. Controlling these parameters is essential to ensure strong and reliable joints.
One critical aspect is the selection of the right welding current and time. The current should be sufficient to create a proper nugget size, while the welding time should allow for complete fusion. Insufficient current or excessively short welding time can result in weak or incomplete welds.
The electrode force applied during spot welding also plays a crucial role in achieving optimal weld quality. Insufficient force can lead to poor contact between the workpieces and electrodes, resulting in uneven heat distribution and weak joints. Conversely, excessive force can cause material deformation or expulsion, affecting both the appearance and strength of the weld.
The cleanliness and surface condition of the workpieces are factors that should not be overlooked. Any contaminants or oxide layers can hinder proper current flow and negatively impact the quality of the weld. Thoroughly cleaning the surfaces before welding, using methods like brushing or chemical treatments, is essential for achieving strong and consistent spot welds.
Spot welding is a versatile joining technique widely used in various industries. Its efficiency, precision, and aesthetic appeal make it suitable for high-volume production while providing strong and durable welds.
Knowing the process, its variations, and factors that influence weld quality is crucial for successful implementation. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this article, manufacturers can ensure optimal spot weld results and achieve reliable and lasting metal joining.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on spot welding! If you’re curious about what spot welding is and how it works, you’ve come to the right place. We’ve compiled the most common questions people have about spot welding and provided detailed answers to help you understand this fascinating process. So let’s dive in!
How does spot welding work?
Spot welding is a process that joins two or more metal pieces together by applying heat and pressure in a specific spot. It works by passing an electrical current through the metal pieces to generate heat, which causes the metal to melt and fuse together. The heat is generated by the resistance to the electrical current flow, and it is concentrated in a small area known as the weld spot. This spot is where the two metal pieces are held together by electrodes, and the intense heat produced melts the metals, forming a solid weld when the current is stopped and pressure is applied.
Spot welding is commonly used in the automotive industry to join car body panels, as well as in manufacturing industries for various metal fabrication processes. It is fast, efficient, and provides a strong bond between the metals, making it a popular choice for many applications.
What are the advantages of spot welding?
Spot welding offers several advantages compared to other welding methods. Firstly, it is a fast process that can join metal pieces quickly, increasing productivity in manufacturing. Secondly, spot welding doesn’t require any additional filler material, making it a cost-effective method. Since it doesn’t use filler material, it also eliminates the need for complex joint preparations.
Furthermore, spot welding produces a strong and durable joint, creating a secure bond between the metal pieces. The process is versatile and can be used with various metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. Additionally, spot welding is automated in many industries, reducing labor costs and ensuring consistent weld quality. Overall, these advantages make spot welding a reliable and efficient method for joining metal parts.
Can spot welding be used on all types of metals?
Spot welding can be used on a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. However, the suitability of spot welding for particular metals depends on their electrical conductivity and melting points. Metals with good electrical conductivity, such as copper and aluminum, are ideal for spot welding as they generate more heat during the process.
On the other hand, materials with poor electrical conductivity, like stainless steel, require higher electrical currents to generate sufficient heat for spot welding. Additionally, metals with vastly different melting points may pose challenges during spot welding, as they may require different welding parameters to ensure a successful bond. Therefore, while spot welding is versatile, it’s important to consider the specific properties of the metals being joined to determine its feasibility.
Can spot welding be done manually?
Spot welding can be performed both manually and with automated machines. Manual spot welding involves using hand-held spot welding guns, where the operator positions the electrodes and triggers the welding current. This method is often used for smaller-scale projects or in situations where automation is not feasible.
However, automated spot welding is more commonly used in industrial settings. Robotic spot welding systems are programmed to perform spot welding operations with high precision and repeatability. They can handle large volumes of welding tasks, ensuring consistent quality and higher productivity. Automated spot welding offers greater efficiency and reduces the risk of human error, making it the preferred choice for large-scale production processes.
Are there any safety considerations for spot welding?
Yes, safety is paramount when performing spot welding. The high heat and electrical currents involved in the process can pose risks. To ensure safety, it’s important to wear appropriate protective gear, such as welding gloves, goggles, and a welding helmet, to shield yourself from sparks, radiant heat, and harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Additionally, proper ventilation is essential to prevent the inhalation of harmful fumes and gases that may be released during spot welding. It’s crucial to work in an adequately ventilated area or use local exhaust ventilation systems to remove welding fumes from the work environment.
Following safety protocols, such as grounding the workpiece and equipment, and adhering to electrical safety guidelines, will help minimize the risks associated with spot welding.
Spot welding is a type of welding that uses heat to join two metal surfaces together. It is commonly used in industries like automotive and construction.
During spot welding, two metal surfaces are pressed together and an electric current is passed through them. This current generates heat, causing the metal to melt and fuse together. Spot welding is fast, efficient, and produces strong, high-quality welds.
The process is used to join metal sheets, wires, and even pipes. It is an important technique in manufacturing because it allows for the rapid production of metal structures and products. Spot welding is a key tool in the world of metalworking!