Welcome to the world of networking, where the OSI Network Layer plays a vital role! So, what are two services provided by the OSI Network Layer? Let’s dive in and find out!
Imagine you’re sending a message to your friend across the country. The OSI Network Layer ensures that your message gets delivered efficiently and reliably by providing two essential services.
The first service is called routing. It’s like having a GPS for your messages, guiding them through the vast network and finding the best path to their destination.
But wait, there’s more! The second service is called logical addressing. Just like how your friend needs to know your address to receive your message, devices on a network need unique addresses too. The OSI Network Layer assigns these addresses, making sure that messages reach their intended destination.
So, with routing and logical addressing, the OSI Network Layer ensures smooth communication across networks. Fascinating, isn’t it? Let’s explore more about these services and how they contribute to the world of networking!
Knowing the Services Provided by the OSI Network Layer
The OSI Network Layer: An Introduction
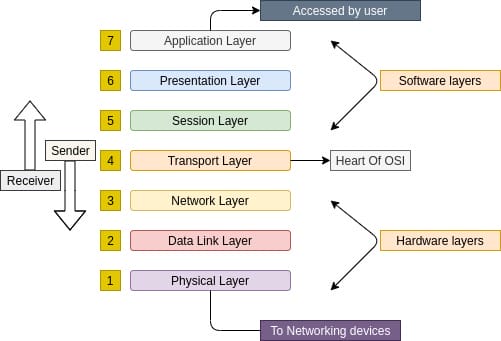
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system into seven distinct layers. Each layer is responsible for specific tasks and provides services to the layer above it. The Network Layer, also known as Layer 3, is a critical component of the OSI model, responsible for enabling end-to-end communication between devices on different networks. It provides services such as addressing, routing, and packet fragmentation.
The Network Layer acts as an intermediary between the transport layer above it and the data link layer below it. It ensures that data packets are properly addressed and routed across networks. The primary services provided by the OSI Network Layer are network addressing and routing.
Network Addressing
Network addressing is the process of assigning unique identifiers to devices on a network. These identifiers, known as IP addresses, enable devices to send and receive data across interconnected networks. The OSI Network Layer provides services for assigning and managing IP addresses, ensuring that each device has a unique identifier within the network. IP addressing allows packets to be routed from the source to the destination, ensuring proper communication between devices.
Routing
Routing is the process of determining the best path for network traffic to travel from the source to the destination. The OSI Network Layer is responsible for selecting and implementing routing protocols that enable efficient and reliable packet delivery. Routing protocols use various algorithms and metrics to make routing decisions based on factors like network congestion, cost, and reliability. The Network Layer ensures that packets are properly routed through different networks to reach their intended destinations.
The Benefits of Network Addressing and Routing
Network addressing and routing, the two key services provided by the OSI Network Layer, play a crucial role in enabling effective communication between devices on interconnected networks. Here are some of the significant benefits of these services:
Efficient Packet Delivery
By providing network addressing and routing services, the OSI Network Layer ensures that packets are delivered efficiently from the source to the destination. The use of unique IP addresses allows for proper identification and tracking of devices, reducing packet loss and optimizing network performance. Routing protocols ensure that packets take the most efficient path across networks, minimizing delays and improving overall communication speed.
Scalability and Flexibility
The ability to assign unique IP addresses to devices and implement routing protocols enables networks to scale and accommodate a large number of devices.
Network addressing ensures that each device can be identified and reached, even in complex network infrastructures. Routing allows for the creation of multiple paths and alternate routes, ensuring flexibility and resilience in the face of network failures or congestion. The OSI Network Layer provides the necessary foundation for building scalable and adaptable network architectures.
Interoperability and Interconnectivity
Standardized network addressing and routing protocols ensure interoperability and interconnectivity between different networks and devices. IP addresses follow a universal format, allowing devices from different vendors and networks to communicate seamlessly.
Routing protocols establish common rules and guidelines for efficient packet routing across networks, regardless of their physical or logical differences. This interoperability and interconnectivity are crucial for creating a cohesive and interconnected global network.
Additional Services Provided by the OSI Network Layer
Traffic Control and Congestion Management
In addition to network addressing and routing, the OSI Network Layer provides services for traffic control and congestion management. Traffic control involves prioritizing and regulating network traffic to ensure the efficient use of available network resources. Congestion management techniques, such as traffic shaping and congestion avoidance, help prevent network congestion and maintain optimal performance. These services enable the OSI Network Layer to effectively handle varying traffic loads and maintain a stable communication environment.
Error Detection and Recovery
The OSI Network Layer also offers services for error detection and recovery. Error detection mechanisms, such as checksums and cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), are used to detect errors in received packets. If errors are detected, the Network Layer can request retransmission of the packet from the source. This ensures data integrity and reliable communication between devices. Error recovery services provided by the OSI Network Layer contribute to the overall reliability and robustness of the network.
Quality of Service (QoS) Management
QoS management is another essential service provided by the OSI Network Layer. QoS refers to the ability of a network to prioritize certain types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications or services receive the necessary bandwidth and latency requirements.
The Network Layer uses QoS mechanisms, such as packet classification, prioritization, and traffic shaping, to allocate network resources effectively. This ensures that important applications, such as voice or video conferencing, receive the appropriate level of service, enhancing the overall user experience.
In conclusion, the OSI Network Layer provides essential services such as network addressing, routing, traffic control, error detection and recovery, and quality of service management.
These services enable efficient and reliable communication between devices on interconnected networks, laying the foundation for a robust and scalable network infrastructure.
By understanding the role of the Network Layer and its services, network administrators and engineers can optimize network performance and ensure seamless connectivity for users.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section on the services provided by the OSI Network Layer. Below, you’ll find answers to some commonly asked questions regarding this topic. If you have any further inquiries, feel free to reach out to us!
What is the OSI Network Layer?
The OSI Network Layer is the third layer in the OSI model and is responsible for providing logical addressing and routing functions. It ensures that data packets are properly sent from the source to the destination across different networks. This layer plays a crucial role in establishing end-to-end connectivity and determining the best route for data transmission.
At this layer, data is encapsulated into packets, and each packet is given a logical network address. The OSI Network Layer takes care of addressing these packets and using routing protocols to determine the optimal path to deliver the packets to their intended destination.
What are the two main services provided by the OSI Network Layer?
The OSI Network Layer provides two primary services: addressing and routing.
Addressing involves assigning a unique logical address to each device or host on a network. These addresses ensure that packets reach the correct destination. By using these addresses, the Network Layer can identify the source and destination of packets, allowing for effective communication across networks.
Routing, on the other hand, deals with determining the best path for data packets to travel from the source to the destination. The Network Layer uses routing protocols to accomplish this task, considering factors such as network congestion, reliability of routes, and destination reachability. Routing ensures that packets are efficiently delivered to their intended recipients, even if they need to traverse multiple networks.
Why is logical addressing important in the OSI Network Layer?
Logical addressing is crucial in the OSI Network Layer as it allows devices to be uniquely identified on a network. It ensures that data packets are sent to the correct destination, preventing confusion and ensuring efficient communication.
With logical addressing, every device or host on a network has a unique identifier or address. This address is used by the Network Layer to direct packets to the desired recipient. By using logical addressing, the Network Layer can distinguish between different devices and route packets accordingly.
How does the OSI Network Layer handle routing?
The OSI Network Layer handles routing by using routing protocols and maintaining routing tables. Routing protocols exchange information between routers, allowing them to determine the best path for data packets to reach their destination. These protocols consider factors such as network congestion, reliability, and destination reachability to make informed routing decisions.
Routers in the Network Layer maintain routing tables, which contain information about known network addresses and the corresponding paths to reach them. When a packet arrives at a router, the Network Layer examines the destination address, consults its routing table, and forwards the packet along the appropriate path. This process continues until the packet reaches its final destination.
What happens when a packet reaches the OSI Network Layer at the destination?
When a packet reaches the OSI Network Layer at the destination, the Network Layer examines the logical address of the packet to determine if it belongs to the local network. If it does, the packet is delivered to the appropriate device within the network. If the packet is meant for another network, the Network Layer forwards the packet to the next hop router based on the routing information in its routing table.
If necessary, the Network Layer may also perform actions such as decapsulation, where the packet is stripped of its Network Layer header to reveal the encapsulated data destined for the upper layers of the OSI model. The packet is then passed to the upper layers for further processing and delivery to the appropriate application.