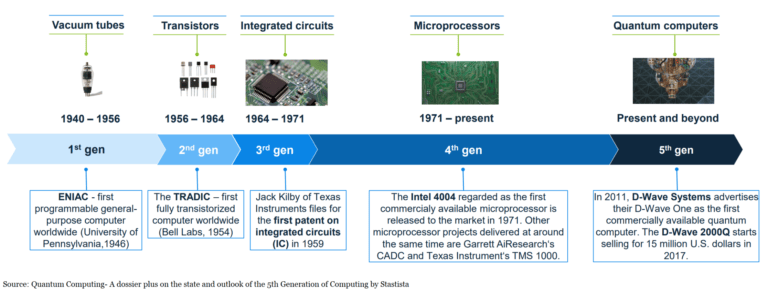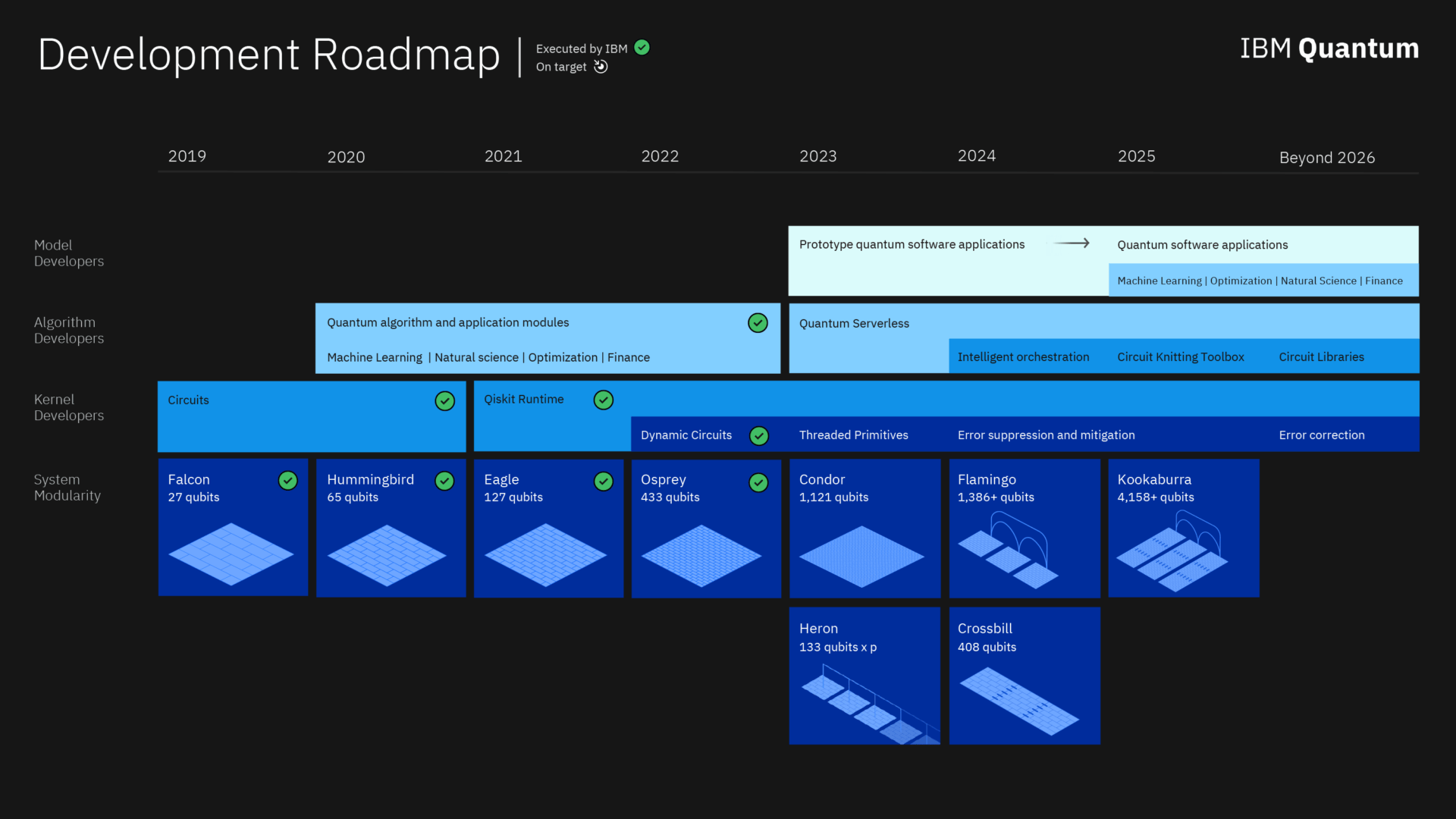
Welcome to the world of quantum computing! Have you ever wondered how many qubits IBM has? Well, you’re in the right place!
Imagine a computer that operates on an entirely different level than the ones we use every day. That’s quantum computing, a revolutionary technology with the potential to solve complex problems faster than ever before.
In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of IBM’s quantum computers and explore just how many qubits they have. So, let’s embark on this quantum adventure together!
How Many Qubits Does IBM Have?
IBM, one of the leading companies in quantum computing, has made significant strides in the field. When it comes to the number of qubits, IBM currently offers various quantum systems with different capacities.
Their most recent quantum processor, IBM Quantum Condor, boasts 65 qubits. It’s important to note that the number of qubits alone does not determine the overall performance and capabilities of a quantum computer.
IBM’s Quantum Journey
IBM’s foray into quantum computing began in 2016 with the launch of IBM Quantum Experience, the world’s first publicly accessible quantum computing platform. Back then, IBM’s quantum systems had a modest number of qubits, typically in the range of 5 to 16 qubits. However, the company has rapidly advanced its technology over the years to push the boundaries of what is possible in the quantum realm.
IBM’s current flagship quantum system is called IBM Quantum System One. This state-of-the-art machine, housed in IBM’s Quantum Computation Center, boasts an impressive qubit count of over 100.
The exact number of qubits is ever-evolving as IBM continues to refine and enhance its quantum hardware, but its prowess in reaching the triple-digit qubit count is a significant milestone in the field of quantum computing.
Qubit Quality and Reliability
While the number of qubits is an important metric for measuring the computational power of a quantum system, it is not the sole determinant of its performance. The quality and reliability of the qubits are equally crucial factors. IBM has made significant strides in improving the quality of its qubits, which directly impacts the system’s ability to perform complex calculations accurately.
IBM’s quantum systems utilize superconducting qubits, which are highly sensitive to disturbances and noise. To mitigate these challenges, IBM has developed cutting-edge technologies, such as error correction codes and quantum error correction techniques.
These advancements help enhance the stability and fidelity of the qubits, thereby enabling more reliable and accurate computations.
Advantages of IBM’s Quantum Systems
IBM’s quantum systems offer several advantages that set them apart in the field of quantum computing. Firstly, the systems are built with scalability in mind, allowing for easy expansion and the addition of more qubits as technology progresses. This scalability paves the way for more complex and larger-scale quantum computations.
Secondly, IBM places great emphasis on fostering a collaborative and open research environment. They provide free access to their quantum systems through the IBM Quantum Experience platform, enabling researchers, developers, and enthusiasts worldwide to explore the potential of quantum computing. This approach has accelerated the pace of innovation and created a vibrant community of quantum enthusiasts.
Lastly, IBM is actively investing in the development of quantum software and algorithms. They offer a suite of quantum development tools, including the Qiskit framework, which simplifies the process of programming and running experiments on their quantum systems. This commitment to software development ensures that users can harness the full potential of IBM’s quantum hardware.
IBM Quantum Roadmap: Towards Exponential Growth
Looking to the future, IBM has an ambitious roadmap for its quantum systems. They are steadfast in their mission to deliver increasingly powerful quantum computers with a higher number of qubits. This will unlock new horizons for computation and enable the execution of more complex quantum algorithms.
IBM’s quantum roadmap also focuses on optimizing the performance of its quantum systems by harnessing the principles of error correction and fault tolerance. By reducing noise and errors, IBM aims to make their quantum computers even more reliable, robust, and suitable for solving real-world problems.
In addition to hardware advancements, IBM is actively involved in quantum education and research. They have collaborated with universities and organizations to establish the IBM Quantum Network, a global initiative that brings together a network of partners to drive progress and advancement in quantum computing collectively.
Advancing the Quantum Frontier
IBM’s journey towards building sophisticated and powerful quantum systems has been nothing short of remarkable. From humble beginnings to surpassing the 100-qubit milestone, IBM continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of quantum computing.
As we move into an era where quantum computers hold the potential to revolutionize various industries, IBM’s dedication to advancing the quantum frontier will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in preparing us for a future powered by quantum computing.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we have compiled some commonly asked questions about the number of qubits IBM has.
How does the number of qubits affect the capabilities of a quantum computer?
The number of qubits in a quantum computer plays a crucial role in determining its capabilities. More qubits mean a greater computational power. With a higher number of qubits, a quantum computer can perform more complex calculations, solve more challenging problems, and simulate quantum systems more effectively.
However, increasing the number of qubits also brings certain challenges, such as maintaining the stability and coherence of the qubits.
Are all qubits in a quantum computer created equal in terms of functionality?
No, all qubits in a quantum computer are not created equal. While all qubits are fundamental units of quantum information, different types of qubits may have varying degrees of reliability and susceptibility to errors.
Quantum computers employ different types of qubits, such as superconducting qubits and trapped ion qubits, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Researchers and engineers are continuously working to improve the quality and performance of qubits to enhance the overall functionality of quantum computers.
Is the number of qubits the only factor to consider when evaluating the capabilities of a quantum computer?
No, the number of qubits is not the only factor to consider when evaluating the capabilities of a quantum computer. While the number of qubits is important for computational power, other factors such as gate errors, coherence time, and connectivity between qubits also play a significant role.
Gate errors refer to errors that occur during operations performed on qubits, while coherence time refers to the duration for which qubits can maintain their quantum state before decoherence takes place.
Connectivity between qubits determines the relationships and interactions that can be established between them. All these factors together contribute to the overall performance and capabilities of a quantum computer.
Is there a limit to the number of qubits that can be created in a quantum computer?
At present, there is no definitive limit to the number of qubits that can be created in a quantum computer. However, as the number of qubits increases, the complexity of controlling and maintaining their quantum properties also intensifies.
This poses various technical challenges, such as mitigating errors, improving stability, and enhancing coherence. Researchers are actively working to overcome these challenges, pushing the boundaries of qubit counts and opening doors to increasingly powerful quantum computers.
So, to sum up, IBM has made quite a few qubits for their quantum computers. Qubits are the building blocks of quantum computers, and IBM has made up to 65 qubits!
These qubits are super tiny and can do amazing things like solve really complex problems faster than regular computers. IBM’s quantum computers are helping scientists and researchers explore new possibilities in technology and science. Who knows what incredible things we’ll be able to do in the future with these powerful machines?