Welcome to the fascinating world of wireless internet! Have you ever wondered how you can access the internet without plugging in a cable? Well, you’re in luck because today we’re going to dive into the question of “How Does Wireless Internet Work?”
Imagine this: you’re sitting in your bedroom, browsing the web on your tablet. But here’s the thing, there are no cables connecting your tablet to the internet. How is that possible? That’s where wireless internet comes into play. It’s like magic!
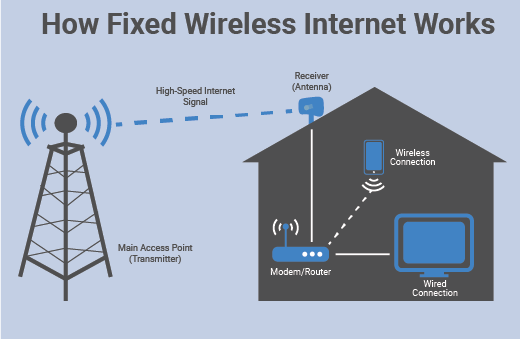
Wireless internet, also known as Wi-Fi, allows us to connect to the internet without using physical cables. Instead, it uses radio waves to transmit data through the air. These radio waves are picked up by a device called a router, which sends and receives signals from your devices, like your tablet or smartphone. So, no more messy cables getting in the way!
Now that we’ve scratched the surface, let’s delve deeper into the wonderful world of wireless internet. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind this incredible technology and discover how it all works. So, let’s jump right in and explore the inner workings of wireless internet!
How Does Wireless Internet Work? A Comprehensive Guide
Wireless internet works by transmitting data through wireless signals instead of using physical cables. Devices, such as smartphones and laptops, connect to a wireless router that sends and receives signals from the internet service provider.
These signals are then converted into data packets that travel through the air to reach the device. The device decodes these packets to retrieve the information. This technology enables convenient internet access without the need for wired connections.
1. Understanding Wireless Communication
Wireless internet relies on the principles of wireless communication, which involves the transmission of data through the air using radio waves.
These radio waves are generated by wireless routers, also known as access points, which convert digital information into analog signals and broadcast them to the surrounding areas.
Devices equipped with wireless network adapters, such as smartphones and laptops, receive these signals and convert them back into digital information that can be understood by the device.
The communication between the access point and the device occurs through specific radio frequencies that are allocated for this purpose.
These frequencies, commonly referred to as wireless bands, are divided into channels to prevent interference between different networks. The devices and access points must be tuned to the same channel to establish a successful connection.
Wireless Standards and Protocols
Wireless internet operates on different standards and protocols, with the most common being Wi-Fi. The Wi-Fi standard is governed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and has evolved over the years to provide faster speeds and improved security.
The different Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax, define the capabilities and features of the wireless network. Each new standard offers advancements in terms of speed, range, and efficiency, allowing for better internet experiences.
2. The Components of a Wireless Network
A wireless network consists of various components working together to enable internet connectivity. Let’s explore the key components and their roles in the wireless ecosystem:
Wireless Router/Access Point
The wireless router, or access point, is the heart of a wireless network. It serves as the central hub that connects devices to the internet and allows them to communicate with each other.
The router connects to the internet through a wired connection, such as a broadband modem, and transmits the internet signal wirelessly using radio waves. It also provides network security features, such as encryption and firewalls, to protect the data transmitted over the network.
Wireless Network Adapter
A wireless network adapter, also known as a Wi-Fi adapter, enables devices to connect to a wireless network. It can be built-in or added externally to devices such as laptops, desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets. The network adapter is responsible for receiving and transmitting the radio signals to establish a connection with the wireless router or access point.
SSID and Password
When setting up a wireless network, you need to configure an SSID (Service Set Identifier) and a password. The SSID is the name of the network that appears when you search for available networks to connect to.
The password, also known as the Wi-Fi password or network key, is a security measure that ensures only authorized users can access your network. It is important to choose a strong password to prevent unauthorized access to your wireless network.
3. Benefits of Wireless Internet
Wireless internet offers numerous benefits that have revolutionized the way we connect and interact with the digital world. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of wireless internet:
Convenience and Mobility
One of the biggest advantages of wireless internet is the freedom to access the internet from anywhere within the range of the wireless network.
Whether you’re at home, in a coffee shop, or at the airport, you can easily connect to the internet without the constraint of physical cables. This mobility allows you to stay connected and productive on the go.
Flexibility and Scalability
Wireless internet provides the flexibility to connect multiple devices to the network without the need for additional wiring. You can connect smartphones, laptops, gaming consoles, smart home devices, and more, all within the same network.
This scalability makes it easy to expand your network and accommodate new devices without the hassle of running cables throughout your home or office.
Simplified Installation
Setting up a wireless network is relatively simple compared to wired networks. With just a few steps, you can connect your wireless router, configure the network settings, and start enjoying internet access. This ease of installation makes wireless internet a popular choice for both residential and commercial environments.
Increased Productivity
Wireless internet enables seamless communication and collaboration between devices, leading to increased productivity. Whether you’re working in a team, attending virtual meetings, or sharing files, wireless internet allows for efficient and instant data transfer. This connectivity empowers businesses and individuals to stay connected and work efficiently in today’s fast-paced digital world.
Wi-Fi Frequency Bands and Channels
Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band offers better range and compatibility with older devices, but it is more susceptible to interference from other devices that use the same frequency, such as microwaves and cordless phones. The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds and less interference but has a shorter range.
Each frequency band is divided into multiple channels to prevent interference between different networks. In the 2.4 GHz band, there are 11 channels available, while the 5 GHz band has more channels, typically 24 or more. It is important to choose the least congested channel to optimize the performance of your wireless network.
Tips for Optimizing Wireless Internet Performance
To ensure the best possible wireless internet experience, consider implementing these tips:
1. Position your wireless router centrally:
Place your router in a central location to maximize coverage and reduce signal loss caused by physical obstacles.
2. Use a strong Wi-Fi password:
Protect your network from unauthorized access by choosing a complex password that includes a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
3. Update your router’s firmware:
Regularly update your router’s firmware to benefit from improved security, bug fixes, and performance enhancements.
4. Optimize your network’s channel:
Use a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to identify the least congested channel and configure your router to operate on that channel.
5. Limit interference:
Keep your router away from devices that can cause interference, such as cordless phones and microwave ovens.
6. Invest in a range extender:
If you have areas with weak Wi-Fi signals, consider using a range extender to expand the coverage of your wireless network.
Wireless internet has transformed the way we connect and communicate, offering unparalleled convenience, flexibility, and productivity.
By understanding the inner workings of wireless communication, the components of a wireless network, and implementing optimization techniques, you can unlock the full potential of wireless internet. So, embrace the wireless revolution and enjoy the freedom of seamless connectivity in today’s digital age!
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section, where we demystify the world of wireless internet. In this section, we will answer some common questions related to how wireless internet works. So, let’s get started!
1. What is wireless internet and how does it work?
Wireless internet, also known as Wi-Fi, allows devices to connect to the internet without the need for cables or physical connections. It works by using radio waves to transmit data between a wireless router or access point and a device such as a smartphone, laptop, or tablet.
The wireless router or access point sends out radio signals, which are picked up by the device’s wireless receiver. These signals contain the data being transmitted, such as web pages, images, or videos. The device then processes this data and displays it on the screen, allowing you to browse the internet wirelessly.
2. What are the advantages of wireless internet?
Wireless internet offers several advantages that make it popular and convenient. Firstly, it provides flexibility and mobility, allowing you to connect to the internet from anywhere within the range of the wireless network.
Secondly, wireless internet eliminates the need for physical connections, making it easy to set up and reducing clutter. It also allows multiple devices to connect to the internet simultaneously, enabling you to have multiple users or devices connected at the same time.
3. How does a wireless router work?
A wireless router acts as the central hub for a wireless network. It connects to the internet through an internet service provider (ISP) and wirelessly transmits data to and from devices within its range.
When a device wants to access the internet, it sends a request to the wireless router. The router then forwards this request to the ISP, which retrieves the requested data and sends it back to the router. The router then transmits the data to the device, allowing it to access the internet.
4. Are there any security concerns with wireless internet?
While wireless internet offers convenience, it is important to consider security measures to protect your network and data. One common security concern is unauthorized access, where someone attempts to connect to your wireless network without permission.
To secure your wireless network, you can set a strong password on your router, use encryption protocols such as WPA2, and hide the network’s name (SSID) to make it less visible to potential intruders. Regularly updating your router’s firmware and using a firewall can also enhance security.
5. What factors can affect the speed and range of wireless internet?
Several factors can impact the speed and range of wireless internet. Distance from the router or access point is a significant factor, as the signal weakens as you move further away. Obstacles such as walls, furniture, or other electronic devices can also interfere with the signal, reducing both speed and range.
The type of wireless technology your devices support can also affect the speed and range. Older devices may only support slower wireless standards, while newer devices can take advantage of faster Wi-Fi standards. Lastly, the number of devices connected to the network simultaneously can impact speed, as the available bandwidth is shared among connected devices.
So, to sum it all up, wireless internet is a way for us to connect to the internet without using wires. It uses signals that are sent and received by devices like routers and smartphones.
These signals travel through the air and allow us to access the internet from anywhere within the range of the network. The signals are transmitted using radio waves, which are a type of electromagnetic wave. And that’s how wireless internet works!
To use wireless internet, we need a device like a router to create a network, and a device like a smartphone or laptop to connect to that network.
The router sends and receives signals to and from our devices, transferring data and allowing us to browse the web, send emails, play games, and do many more things online.
It’s important to remember that wireless internet has a limited range, so we need to be within that range to stay connected. And that’s the basic idea behind wireless internet!