What is the Relationship Between Privacy and Security Within Cybersecurity?
When it comes to the exciting world of cybersecurity, there is one question that often comes up: what is the relationship between privacy and security? It’s an important question to explore because, in this digital age, protecting our personal information and maintaining our privacy is more crucial than ever.
So, let’s dive in and discover how these two concepts interconnect and impact our online lives!
When we talk about privacy and security in the context of cybersecurity, we’re essentially looking at two sides of the same coin. Privacy involves safeguarding our personal data and ensuring that it remains confidential, while security focuses on protecting our information and systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats. The relationship between privacy and security is symbiotic – they work hand in hand to create a safe and protected online environment.
In today’s interconnected world, privacy and security are intertwined like peanut butter and jelly. Without proper security measures in place, our private information becomes vulnerable to hackers and online threats. And, without privacy protections, our security defenses are weakened, leaving us exposed to potential breaches.
So, whether we’re discussing securing our financial transactions, protecting our social media accounts, or even just browsing the internet, understanding the relationship between privacy and security is key to staying safe in the digital landscape.
The Relationship Between Privacy and Security Within Cybersecurity: Explained
As technology continues to advance, the importance of privacy and security within the realm of cybersecurity has become increasingly paramount.
In today’s digital age, where personal information is constantly being shared, stored, and transmitted, it is essential to understand the relationship between privacy and security.
This article will delve into the intricacies of this relationship, exploring how these two concepts intersect and influence one another within the context of cybersecurity.
The Importance of Privacy in Cybersecurity
Privacy is the fundamental right to control one’s personal information, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
This concept is critical within the field of cybersecurity because it establishes the groundwork for maintaining trust between users and the systems they interact with. When privacy is compromised, individuals can experience significant consequences, such as identity theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and more.
To ensure privacy in the digital landscape, cybersecurity practices must include measures such as data encryption, secure communication channels, access controls, and user consent mechanisms. By implementing these measures, organizations and individuals can protect personal information from falling into the wrong hands, safeguarding the privacy of users and fostering trust in the online environment.
Furthermore, privacy regulations and laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, play a crucial role in reinforcing privacy rights and holding organizations accountable for the handling of personal data. By adhering to these regulations, businesses and institutions demonstrate their commitment to protecting privacy and mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and cyber threats.
The Role of Security in Cybersecurity
While privacy focuses on protecting personal information, security encompasses a broader scope, encompassing the safeguarding of systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Security measures are essential to defend against a wide range of cyber threats, including hacking, malware, phishing attempts, and other malicious activities.
Cybersecurity professionals employ various security measures and practices to ensure the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information.
These include network security protocols, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, multifactor authentication, and regular system updates.
By implementing these security measures, organizations can fortify their defenses, detect and respond to threats promptly, and maintain the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data.
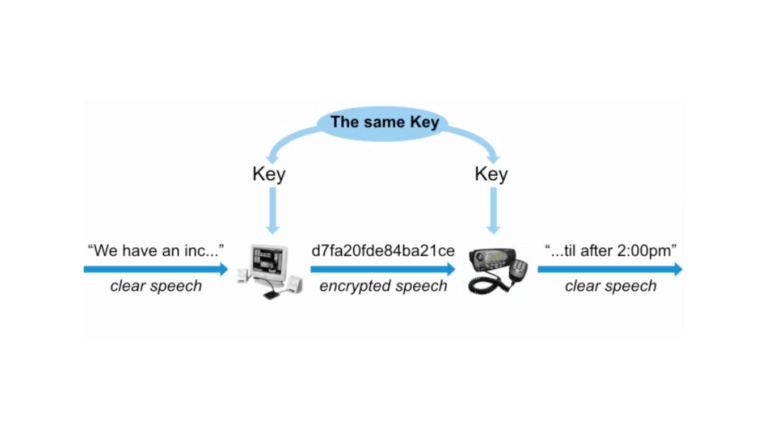
The relationship between privacy and security is symbiotic, as security measures protect individual privacy by preventing unauthorized access to confidential information.
Robust security measures also help foster trust among users, as they provide reassurance that their personal data is being adequately safeguarded. Without robust security controls, privacy cannot be guaranteed, as even well-intentioned mishaps or vulnerabilities can result in breaches and compromises.
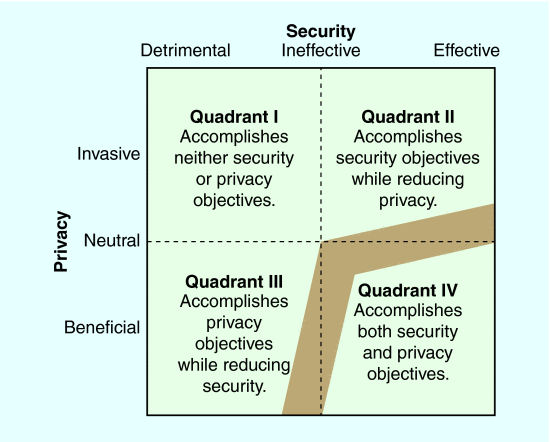
1) Balancing Privacy and Security: Finding the Sweet Spot
While privacy and security are inherently linked, there can sometimes be tension between the two. Striking the right balance between protecting privacy and implementing security measures is crucial.
Too much emphasis on security can impede privacy and erode user trust, while an excessive focus on privacy may lead to lax security measures and make systems vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Organizations must adopt a privacy-by-design approach, integrating privacy protections into the framework of their systems and processes while ensuring that security measures do not compromise the user’s privacy.
This involves conducting privacy impact assessments, implementing privacy-enhancing technologies, and regularly reviewing and updating privacy policies to align with evolving regulations and best practices.
Ultimately, finding the sweet spot between privacy and security requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving professionals with expertise in both fields to collaborate and strike the right balance that protects individuals’ privacy while maintaining strong security defenses.
2) The Benefits of an Integrated Approach to Privacy and Security
When privacy and security are integrated into the fabric of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy, several benefits arise. Firstly, users gain confidence in their interactions with a system or service, knowing that their privacy is respected and their data is secure. This confidence encourages higher levels of engagement, increased usage, and improved customer satisfaction.
Secondly, an integrated approach ensures compliance with privacy regulations and minimizes the risk of legal repercussions resulting from data breaches or mishandling of personal information.
By aligning security practices with privacy requirements, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting privacy, foster trust in their brand, and mitigate the potential financial and reputational damage associated with privacy violations.
Lastly, an integrated approach to privacy and security leads to a proactive rather than a reactive stance, allowing organizations to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats before they are exploited.
By conducting regular risk assessments, implementing robust security controls, and ensuring privacy best practices are followed, organizations can stay one step ahead of cyber threats and protect both their users’ privacy and their own business interests.
3) Privacy and Security in the Era of Emerging Technologies
As emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain continue to reshape the digital landscape, the relationship between privacy and security becomes even more critical. These technologies bring immense opportunities but also pose new challenges concerning data privacy and security.
AI, for example, possesses the potential to revolutionize industries and improve user experiences. However, it also relies heavily on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy.
Organizations need to apply privacy-preserving techniques and implement robust security measures to ensure that AI systems are trustworthy and respectful of user privacy.
The IoT, which connects various devices and systems, creates a vast network of interconnected data, elevating the importance of security to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation of sensitive information. Privacy controls must also be implemented to ensure that users have control over their data and consent to its collection and use.
Similarly, blockchain, while offering the promise of secure and transparent transactions, also presents challenges in terms of privacy.
Organizations must strike a balance between the inherent transparency of blockchain and the privacy requirements of users, particularly in contexts where sensitive information needs to be protected.
4) The Responsibility of Individuals in Protecting Privacy and Security
While organizations play a significant role in ensuring privacy and security within cybersecurity, individuals also have a responsibility to protect their own personal information. Adopting good cybersecurity practices can go a long way in safeguarding privacy.
Individuals should prioritize the use of strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication whenever possible, be cautious when sharing personal information online, and regularly update their devices and software to ensure the latest security patches are installed.
Additionally, individuals should familiarize themselves with privacy settings on social media platforms and ensure they are appropriately configured to limit the sharing of personal information with unintended audiences.
By taking these proactive steps, individuals can minimize the risk of privacy breaches and contribute to a safer and more secure digital environment.
Key Takeaways: What is the Relationship Between Privacy and Security Within Cybersecurity?
- Privacy and security are closely intertwined within the field of cybersecurity.
- Privacy refers to the protection of personal information, while security encompasses the measures taken to safeguard systems and data.
- Achieving a balance between privacy and security is crucial in cybersecurity efforts.
- Privacy is necessary for maintaining trust and ensuring individuals’ rights are respected.
- Security measures such as encryption and firewalls help protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on the relationship between privacy and security within cybersecurity. Here, we’ll answer some common questions related to this topic. Read on to learn more!
1. Why is privacy important in cybersecurity?
Privacy is crucial in cybersecurity because it protects individuals and organizations from unauthorized access to their sensitive information.
When privacy is compromised, personal data, financial details, and other confidential information can be exposed, leading to various risks, such as identity theft and fraud. By maintaining strong privacy measures, cybersecurity ensures that personal and sensitive information remains secure, increasing trust and confidence in online interactions.
Moreover, privacy is closely linked to individual rights and freedoms. It allows individuals to control their personal data and make informed choices about how it is collected, stored, and shared. Without privacy, we would be vulnerable to constant surveillance and potential misuse of our information, undermining our autonomy and human rights in the digital age.
2. How does security protect privacy in cybersecurity?
Security measures within cybersecurity help protect privacy by safeguarding data from unauthorized access, theft, or manipulation. These measures include using strong and unique passwords, encryption techniques, access controls, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
By implementing these security measures, organizations and individuals can ensure that their information remains confidential and secure.
Additionally, security practices such as regular software updates, vulnerability testing, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices can help prevent data breaches and cyberattacks. By maintaining robust security protocols, the risk of privacy breaches is reduced, enabling individuals to have greater control over their personal information and maintaining trust in the digital ecosystem.
3. How does privacy impact cybersecurity regulations and policies?
Privacy concerns have a major influence on the development and enforcement of cybersecurity regulations and policies.
Governments and regulatory bodies recognize the need to protect personal information and often impose specific requirements on organizations to ensure privacy and security. These regulations may include data protection laws, breach notification requirements, and guidelines for handling personally identifiable information (PII).
By establishing clear privacy regulations and policies, governments aim to create a framework that incorporates security measures while respecting individuals’ privacy rights. These regulations not only protect individuals but also promote responsible data-handling practices among organizations, contributing to a more secure cybersecurity landscape.
4. What are some common privacy and security vulnerabilities in cybersecurity?
Several common vulnerabilities can compromise privacy and security in cybersecurity. These include weak passwords or password reuse, outdated software with known vulnerabilities, phishing attacks, social engineering, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Additionally, the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has introduced new entry points for cyber threats, as these devices often lack sufficient security measures.
Furthermore, insufficient user awareness and education about cybersecurity practices can make individuals more susceptible to privacy and security risks.
It’s important to stay vigilant and regularly update security software, use strong and unique passwords, and be cautious of suspicious emails or links to minimize vulnerabilities and protect both privacy and security.
5. How can individuals protect their privacy and security in cybersecurity?
Individuals can take several steps to protect their privacy and security in cybersecurity. Firstly, they should use strong, unique passwords for all devices and online accounts.
Regularly updating software and promptly installing security patches is also crucial to patch any known vulnerabilities.
In addition, individuals should be wary of phishing attempts and social engineering tricks, such as clicking on suspicious links or providing personal information to untrusted sources. It’s also advisable to use secure Wi-Fi networks and enable encryption protocols when transmitting sensitive data.
Lastly, staying informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices is essential. By educating themselves on common risks and employing proper security measures, individuals can enhance their privacy and security in the digital realm.
Privacy and security are closely related in cybersecurity. Privacy refers to keeping personal information safe, while security focuses on protecting systems and data from threats. Both are vital for ensuring online safety.
When privacy is compromised, our personal information can be accessed by strangers, leading to identity theft or other harmful consequences.
On the other hand, without strong security measures, hackers and cybercriminals can breach systems, steal data, and cause disruptions. Maintaining a balance between privacy and security is crucial to safeguarding ourselves online.
To achieve this balance, we need to use strong passwords, be cautious about sharing personal information, and regularly update our software and devices.
By being mindful of our online actions and taking necessary precautions, we can enjoy the benefits of the internet while keeping ourselves safe. So, remember: protect your privacy and strengthen your security for a safer online experience!