Have you ever wondered how devices like smartphones and navigation systems determine our GPS coordinates? It’s a fascinating process that allows us to pinpoint our exact location on Earth.
In this article, we’ll explore the inner workings of GPS technology and uncover the secrets behind how devices determine GPS coordinates. So, let’s dive in and uncover the magic behind this incredible technology.
GPS, which stands for Global Positioning System, is a network of satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites constantly send out signals that our devices can pick up.
By receiving signals from multiple satellites, our devices can calculate our precise position. But how do they actually do it? That’s what we’re here to find out!
We’ll explore the concepts of trilateration, satellite geometry, and the role of time in determining GPS coordinates. So, let’s get started on this exciting journey into the world of GPS technology!
GPS coordinates play a crucial role in our daily lives, whether it’s finding directions, tracking fitness activities, or even catching rare Pokémon in augmented reality games.
Knowing how devices determine GPS coordinates will not only satisfy your curiosity but also give you a deeper appreciation for the technology that makes it all possible. So, get ready to unlock the mysteries of GPS and discover the wonders of navigation!
How Do Devices Determine GPS Coordinates?
Ever wondered how your devices determine GPS coordinates? It’s a fascinating process. Your device uses a network of satellites to triangulate your position on the Earth’s surface. By calculating the time it takes for signals to travel from multiple satellites to your device, it can pinpoint your location. This information is then converted into latitude and longitude coordinates. It’s a complex yet amazing system that allows us to navigate and explore the world around us.
Role of Satellites in Determining GPS Coordinates
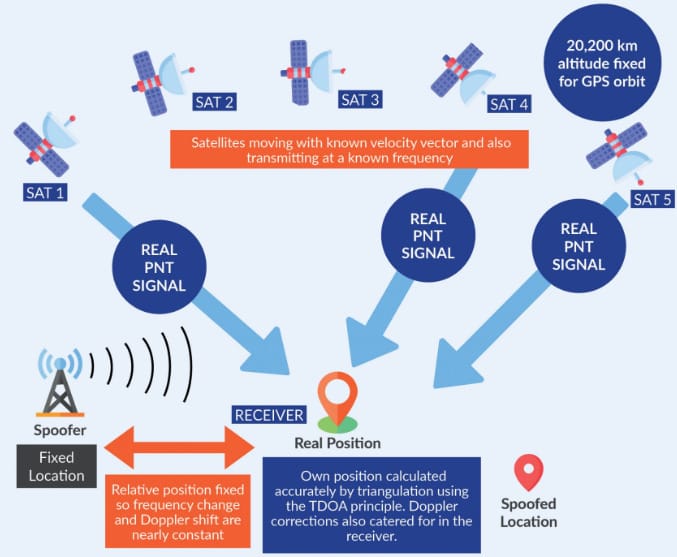
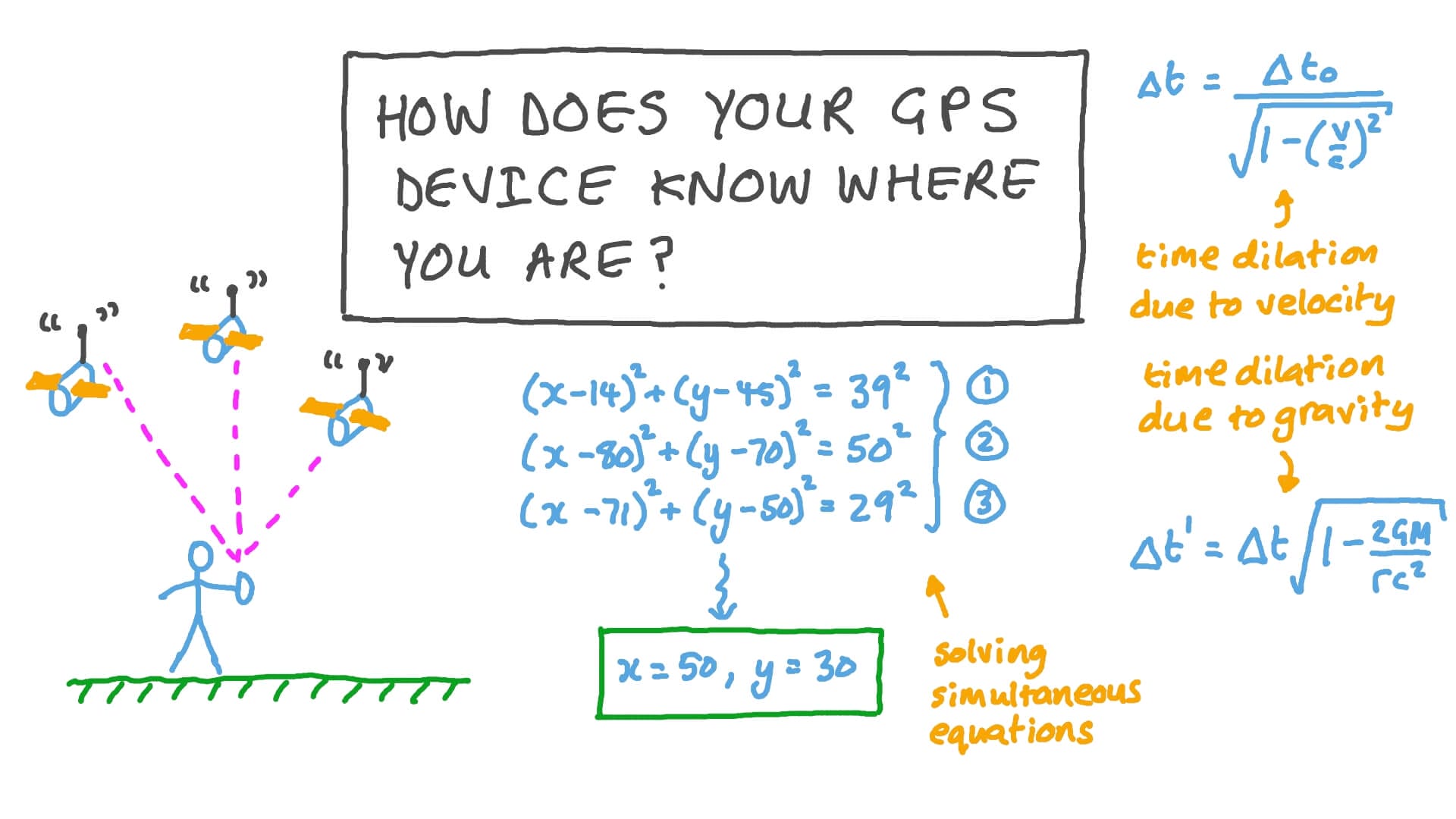
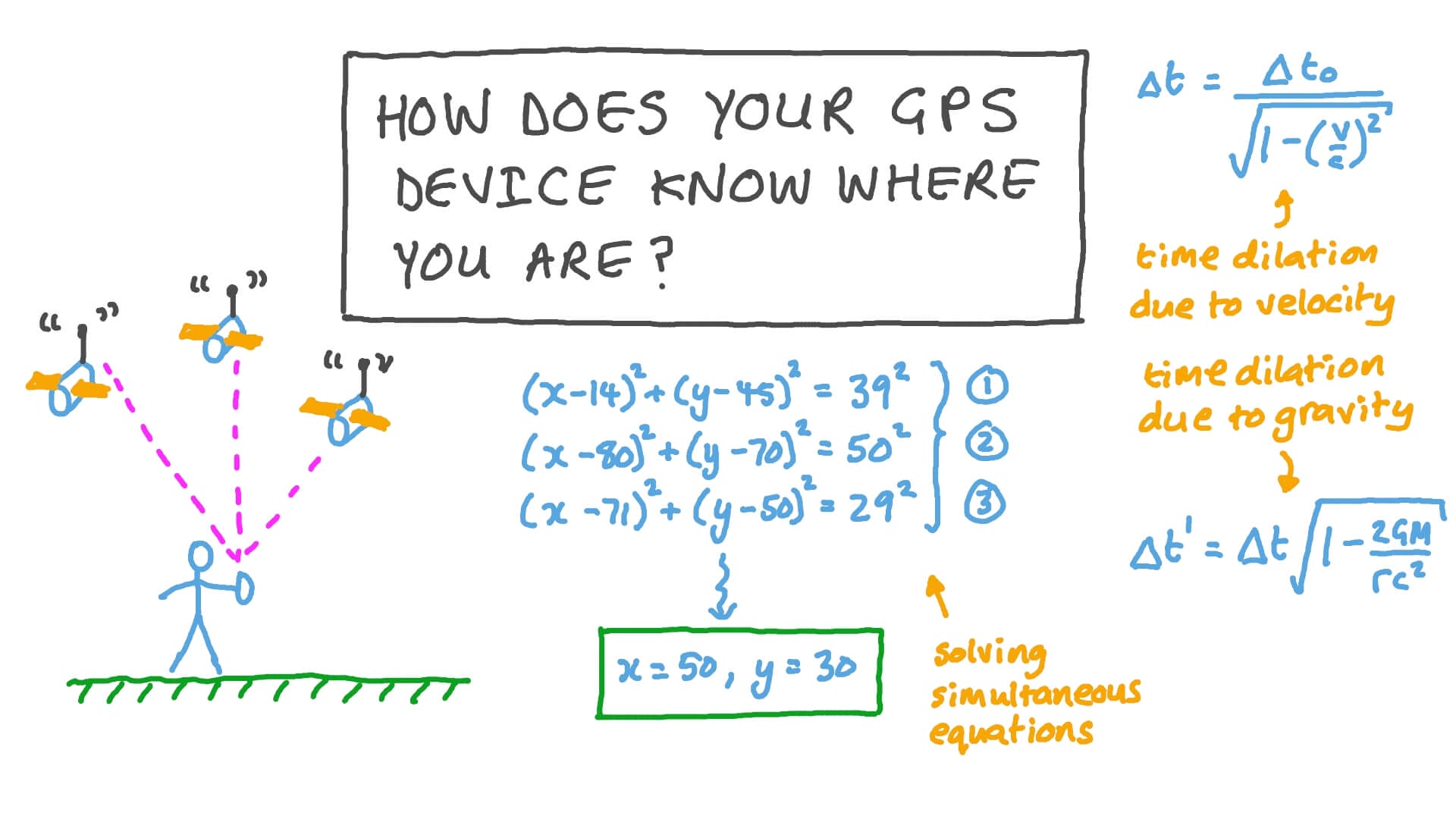
One of the key components in determining GPS coordinates is the use of satellites. GPS devices communicate with a network of satellites that orbit the Earth, constantly transmitting their location and the exact time.
By receiving signals from multiple satellites, the GPS device can accurately calculate the user’s coordinates. The distance between each satellite and the device is determined by the time it takes for the signal to travel. These signals are then used to triangulate the user’s position on the Earth’s surface.
GPS satellites are strategically positioned around the Earth and work in harmony to ensure accurate positioning.
Currently, there are around 30 satellites in orbit that are part of the GPS network, and this number is constantly being updated and expanded.
These satellites transmit their signals in the form of radio waves, which can penetrate through clouds, buildings, and other obstacles, making them easily accessible to GPS devices.
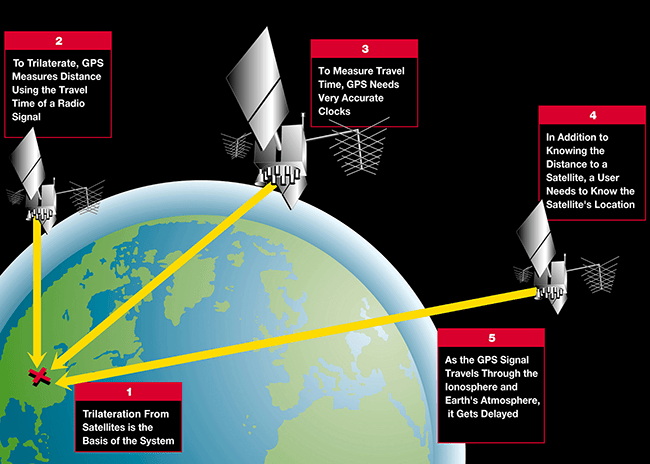
The Trilateration Process in Determining GPS Coordinates
Once the GPS device receives signals from multiple satellites, it begins the process of trilateration to determine the user’s exact location.
Trilateration involves measuring the distances between the device and each satellite based on the time it took for the signals to travel. Using this information, the GPS device can calculate the user’s position by overlapping the spheres created by the distances measured from each satellite.
Imagine each satellite as a point in space with the device at the center of a sphere. The intersection point of these spheres represents the user’s location on the Earth’s surface. By using data from at least four satellites, the device can determine the user’s latitude, longitude, and altitude.
This data is then processed by the device’s software, which converts it into the recognizable GPS coordinates that we see on our screens.
The Integration of Other Technologies in GPS Devices
While satellites play a crucial role in determining GPS coordinates, they are not the only technology involved in this process.
Modern GPS devices often integrate other technologies to enhance accuracy and provide additional features. One such technology is Assisted GPS (A-GPS), which utilizes mobile networks to assist in the location process.
A-GPS works by sending information from the device to a server via the mobile network. This server, in turn, determines the position of the satellites in real time and provides this information back to the device. By combining this data with signals from satellites, the device can calculate coordinates more quickly and with greater accuracy, especially in areas where satellite signals may be weak or obstructed.
Furthermore, some GPS devices incorporate Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) that use a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers to provide a continuous stream of data on the device’s movement and orientation.
This additional information helps to reduce errors in determining GPS coordinates caused by signal interruptions or temporary loss of satellite connections.
Improving GPS Accuracy with Differential GPS
Differential GPS (DGPS) is a technique used to further enhance the accuracy of GPS coordinates. DGPS takes into account the errors introduced by various factors such as atmospheric conditions and satellite clock deviations.
This technique requires the use of a reference station located at a known position and equipped with a high-precision GPS receiver.
The reference station continuously monitors the GPS signal and calculates the errors experienced at its location. This information is then transmitted to the GPS devices in the area, allowing them to correct their calculations and improve accuracy.
DGPS can significantly reduce position errors, especially in environments where a high level of precision is required, such as marine and aviation applications.
Benefits of GPS Technology
The advancements in GPS technology have revolutionized the way we navigate and explore the world. Here are some of the key benefits of using GPS devices:
1. Accurate navigation: GPS devices provide precise coordinates, allowing users to navigate with confidence and accuracy, whether on foot, in a vehicle, or during outdoor activities like hiking or boating.
2. Time-saving: By providing real-time information about the fastest routes, traffic conditions, and alternative options, GPS devices help optimize travel time, leading to efficient journeys.
3. Safety and security: GPS devices can be invaluable during emergencies, allowing users to quickly share their location and summon assistance. They are also used in tracking systems for vehicles and other valuable assets.
4. Outdoor exploration: GPS devices enable outdoor enthusiasts to explore remote areas confidently, as they can accurately track their positions, mark waypoints, and plan routes.
5. Fitness and health tracking: Many GPS devices are equipped with fitness tracking features, enabling users to monitor their distance, speed, and other metrics during workouts, helping them achieve their fitness goals.
GPS devices determine coordinates by utilizing a network of satellites, trilateration, and the integration of other technologies to enhance accuracy and functionality.
With their ability to provide accurate navigation, save time, ensure safety, and enhance outdoor exploration, GPS devices have become an indispensable tool in our modern lives.
So, next time you use your GPS device to find your way, remember the intricate process behind how it determines your exact location on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Looking to understand how devices determine GPS coordinates? Read our collection of frequently asked questions for answers that break down the process in a simple and engaging way.
How does GPS work on a smartphone?
Smartphones determine GPS coordinates through a network of satellites. These satellites transmit signals that are received by the smartphone’s GPS receiver.
The receiver then calculates the distance between the smartphone and at least four satellites, using the time it took for the signals to reach the receiver. By triangulating these distances, the smartphone can determine its precise GPS coordinates, including latitude, longitude, and altitude.
Additionally, smartphones often use other technologies, such as cellular networks and Wi-Fi, to enhance the accuracy and speed of GPS location determination.
These technologies provide additional reference points that help the smartphone quickly calculate its position and improve accuracy, especially in urban environments with tall buildings or limited satellite visibility.
Can GPS work without an internet connection?
Yes, GPS can work without an internet connection. GPS devices, including smartphones, can connect directly to GPS satellites to determine their coordinates.
Unlike navigation apps that require an internet connection for map data, GPS relies solely on satellite signals, making it possible to use GPS offline, even in remote areas without internet access.
However, without an internet connection, the device may not be able to download the latest maps and information. It’s essential to download offline maps in advance or use a GPS-enabled device that has preloaded maps to ensure accurate navigation even when offline.
How do GPS devices determine altitude?
GPS devices determine altitude by leveraging the signals transmitted by GPS satellites. In addition to providing latitude and longitude, GPS satellites also send information about the distance of the satellite from the Earth’s center.
By measuring the time it takes for the signal to travel from the satellite to the GPS device, the device can calculate the distance between the two. This distance, combined with the device’s known height above sea level, allows it to determine the device’s altitude accurately.
However, it’s important to note that altitude calculations can be affected by various factors such as atmospheric conditions and the position of the satellites.
As a result, GPS altitude readings may not always be as accurate as latitude and longitude coordinates. For more precise altitude measurements, devices may integrate additional sensors, such as barometric sensors, which can help compensate for these limitations.
Why do GPS devices sometimes show inaccurate coordinates?
There are several reasons why GPS devices may show inaccurate coordinates. One common reason is the presence of obstacles that obstruct the signals from GPS satellites.
Tall buildings, dense forests, or even being indoors can create signal blockages, resulting in decreased accuracy or loss of GPS signal altogether.
Additionally, certain atmospheric conditions, such as solar flares and ionospheric disturbances, can affect the signals sent by GPS satellites. These disruptions can introduce errors in GPS calculations, leading to inaccurate coordinates.
Lastly, GPS devices may also experience inaccuracies if the receiver itself is of low quality or if there is interference from other electronic devices in the vicinity.
How accurate are GPS coordinates?
The accuracy of GPS coordinates can vary depending on various factors, including the quality of the GPS receiver, the number of satellites in view, and the environmental conditions.
In ideal conditions with a clear view of multiple satellites, GPS devices can provide location accuracy within a few meters, sometimes even down to a few centimeters.
However, in challenging environments where satellite visibility is limited or obstructed, such as in urban areas or dense forests, GPS accuracy may decrease. Under such conditions, accuracy can range from a few meters up to several tens of meters.
For most day-to-day activities, GPS accuracy within a few meters is typically sufficient, but certain applications, such as precise surveying or navigation in hazardous terrains, may require higher accuracy and specialized equipment.
GPS devices use a network of satellites to determine our exact location on Earth. These satellites send signals to our devices, which calculate our coordinates based on the time it takes for the signals to reach us. The GPS system uses trilateration to pinpoint our location by measuring the distance between us and multiple satellites.
It’s like a game of “hot and cold” where our device tries to get closer to the satellites’ signals to find where we are. Once our position is determined, our devices can provide accurate navigation and location-based services.
GPS coordinates consist of latitude and longitude, which help us identify any point on the planet. Latitude tells us how far north or south we are from the equator, while longitude indicates our distance east or west from the Prime Meridian.
With these coordinates, we can find directions, explore new places, and even play location-based games. GPS technology has revolutionized navigation and made it easier for us to explore the world around us, all thanks to the satellites and the clever calculations happening inside our devices.