Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that operates outside the control of banks and governments. It was created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group of people known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network and uses cryptography to secure transactions.
The Basics of Bitcoin
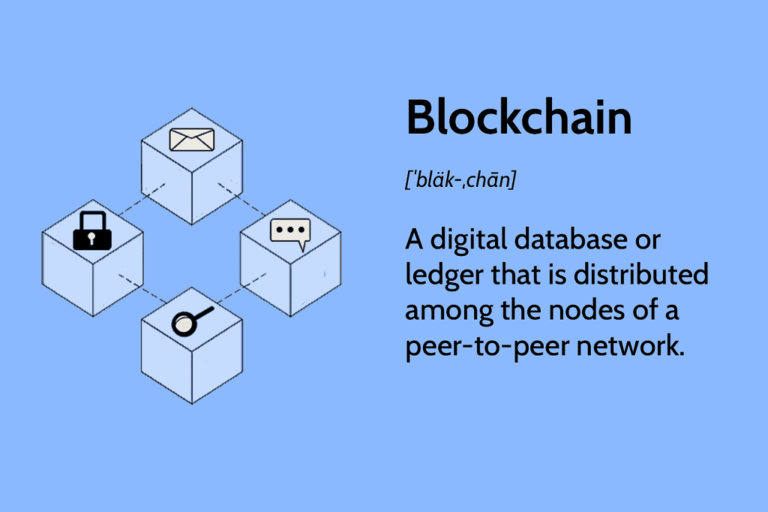
Bitcoin is not a physical currency like coins or bills. Instead, it exists solely in digital form. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers known as nodes. These nodes work together to validate and secure transactions.
Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin is not issued or controlled by a central authority. Instead, new Bitcoins are created through a process called mining. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. In return for their efforts, miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins.
How Bitcoin Transactions Work
When someone wants to send Bitcoin to another person, they create a transaction. This transaction includes the recipient’s public key, which is a unique string of characters that identifies their Bitcoin address. The sender signs the transaction with their private key, which is a secret code that proves ownership of the Bitcoins being sent.
Once the transaction is created, it is broadcast to the network and picked up by the nodes. The nodes verify the transaction by checking that the sender has sufficient Bitcoins and that the transaction is valid. Once verified, the transaction is added to a block, which is then added to the blockchain.
Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, meaning once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it cannot be reversed or altered. This provides security and prevents fraud.
The Role of Miners in the Bitcoin Network
Miners play a crucial role in the Bitcoin network. Their primary function is to validate and secure transactions. As mentioned earlier, miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems. These problems require significant computational power and energy consumption.
When a miner successfully solves a problem, they create a new block of transactions and add it to the blockchain. In return, they are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins. The mining process also helps to secure the network by making it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate transactions.
Over time, the mining process becomes more challenging as the network adjusts the difficulty level to maintain a consistent rate of block creation. This ensures that new Bitcoins are not created too quickly and helps to control inflation.
The Limitations of Bitcoin
While Bitcoin has gained popularity and recognition, it does have some limitations. One of the main concerns is scalability. The Bitcoin network can process a limited number of transactions per second, which can lead to delays and higher fees during periods of high demand.
Another concern is the energy consumption associated with Bitcoin mining. The process requires a significant amount of electricity, leading to environmental concerns. Efforts are being made to develop more energy-efficient mining methods and to explore alternative consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake.
Bitcoin’s volatility is also a point of concern. The price of Bitcoin can fluctuate dramatically in short periods, making it a risky investment and less stable as a store of value compared to traditional currencies.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has come a long way since its creation in 2008. It has gained widespread recognition and acceptance as a form of payment by various businesses and individuals. Many see Bitcoin as a potential hedge against inflation and a store of value in uncertain economic times.
As the technology and infrastructure around Bitcoin continue to evolve, it is expected to become more accessible and user-friendly. This could lead to increased adoption and further integration into the traditional financial system.
However, challenges and regulatory hurdles remain. Governments around the world are still grappling with how to regulate and tax cryptocurrencies. The future of Bitcoin will depend on how these issues are addressed and whether it can maintain its decentralized nature while also becoming more widely accepted.
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that operates on a peer-to-peer network. It uses cryptography to secure transactions and is maintained by a network of computers called nodes. Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain.
Miners play a crucial role in the Bitcoin network by validating and securing transactions. They are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins for their efforts. However, Bitcoin has limitations, including scalability issues, energy consumption concerns, and price volatility.
Despite these challenges, Bitcoin has gained recognition and acceptance as a form of payment and a potential store of value. Its future will depend on how it addresses regulatory hurdles and continues to evolve as a technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bitcoin
1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency created in 2009 by an unknown person using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers.
2. How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded on a public ledger called a blockchain. The Bitcoin network is maintained by miners who solve complex mathematical problems.
3. What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions on the Bitcoin network and adding them to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex algorithms and are rewarded with Bitcoin.
4. Is Bitcoin Legal?
The legality of Bitcoin varies by country. In some jurisdictions, it is fully legal, while in others, it is either restricted or banned.
5. How Can I Buy Bitcoin?
You can buy Bitcoin through various platforms like cryptocurrency exchanges, Bitcoin ATMs, or directly from other individuals via P2P platforms.
6. Is Bitcoin Safe?
Bitcoin is generally considered safe due to its cryptographic security features. However, it’s essential to use reputable wallets and exchanges and follow best practices for securing your assets.
7. What is a Bitcoin Wallet?
A Bitcoin wallet is a digital storage space where you can securely keep your Bitcoin. Wallets can be online, offline, hardware-based, or even paper-based.
8. How is Bitcoin Different from Traditional Currencies?
Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat), Bitcoin is decentralized and operates on a peer-to-peer network.
9. Can I Make Money with Bitcoin?
Yes, many people have profited from Bitcoin’s price volatility. However, investing in Bitcoin carries risks and should be approached cautiously.
10. What is the Current Price of Bitcoin?
The price of Bitcoin fluctuates constantly due to market demand and supply. You can check real-time prices on various cryptocurrency exchanges.
11. How Many Bitcoins Are There?
As of 2021, there are 18.8 million Bitcoins in circulation, with a maximum supply of 21 million.
12. What is Bitcoin Cash?
Bitcoin Cash is a fork of Bitcoin that was created to increase the block size, allowing for more transactions to be processed.
13. What is a Bitcoin Faucet?
A Bitcoin faucet is a website that gives away small amounts of Bitcoin for free, usually as a way to introduce new users to the cryptocurrency.
14. Can Bitcoin Transactions Be Reversed?
No, Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. Once confirmed, they cannot be undone.
15. What are Bitcoin Confirmations?
Bitcoin confirmations are the number of times a transaction is verified by the network. More confirmations mean higher transaction security.
16. What is a Bitcoin Node?
A Bitcoin node is a computer that participates in the Bitcoin network by maintaining a copy of the blockchain and validating transactions.
17. What is the Bitcoin Halving?
The Bitcoin halving is an event where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, effectively reducing the rate at which new Bitcoins are created.
18. How Do I Send and Receive Bitcoin?
You can send and receive Bitcoin using your Bitcoin wallet. Transactions are initiated by sending Bitcoin from one wallet address to another.
19. What is a Bitcoin Address?
A Bitcoin address is a string of characters used to receive Bitcoin. It is like a bank account number for your Bitcoin wallet.
20. What is a Bitcoin Private Key?
A Bitcoin private key is a secret code used to access and manage your Bitcoin. It should be kept confidential.
21. What is a Bitcoin Public Key?
A Bitcoin public key is derived from the private key and is used to create wallet addresses.
22. What is a Bitcoin Exchange?
A Bitcoin exchange is a platform where you can buy, sell, or trade Bitcoin using various currencies.
23. What is Bitcoin’s Market Cap?
Bitcoin’s market cap is the total value of all Bitcoins in circulation, calculated by multiplying the current price by the total number of Bitcoins.
24. What is a Bitcoin ETF?
A Bitcoin ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) is a financial product that tracks the price of Bitcoin and can be traded on traditional stock exchanges.
25. What is a Bitcoin Futures Contract?
A Bitcoin futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell Bitcoin at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future.
26. What is Bitcoin Scalability?
Bitcoin scalability refers to the network’s ability to handle and process large numbers of transactions.
27. What is a Bitcoin Block?
A Bitcoin block is a collection of transactions that have been verified and added to the blockchain.
28. What is the Bitcoin Genesis Block?
The Bitcoin Genesis Block is the first block in the Bitcoin blockchain, created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009.
29. What is a Bitcoin Transaction Fee?
A Bitcoin transaction fee is a small amount paid to miners for processing a Bitcoin transaction.
30. What is a Bitcoin Mixer?
A Bitcoin mixer is a service that mixes your Bitcoins with others to obscure the transaction history.
31. What is a Bitcoin API?
A Bitcoin API (Application Programming Interface) allows developers to interact with the Bitcoin network.
32. What is Bitcoin Arbitrage?
Bitcoin arbitrage involves buying Bitcoin at a low price on one exchange and selling it at a higher price on another.
33. What is a Bitcoin Bull Market?
A Bitcoin bull market is a period of rising Bitcoin prices.
34. What is a Bitcoin Bear Market?
A Bitcoin bear market is a period of falling Bitcoin prices.
35. What is a Bitcoin Cold Wallet?
A Bitcoin cold wallet is an offline storage method for keeping your Bitcoin secure.
36. What is a Bitcoin Hot Wallet?
A Bitcoin hot wallet is an online storage method, more convenient but less secure than a cold wallet.
37. What is Bitcoin Leverage?
Bitcoin leverage allows you to control a large position with a small amount of capital, increasing both potential profits and risks.
38. What is a Bitcoin Derivative?
A Bitcoin derivative is a financial contract whose value is derived from the price of Bitcoin.
39. What is a Bitcoin Smart Contract?
A Bitcoin smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms directly written into code.
40. What is a Bitcoin Whitepaper?
The Bitcoin Whitepaper is the original document written by Satoshi Nakamoto, outlining the purpose and mechanics of Bitcoin.
41. What is a Bitcoin Airdrop?
A Bitcoin airdrop is a distribution of Bitcoin or a related token, usually for free, to holders of a particular asset.
42. What is a Bitcoin Fork?
A Bitcoin fork is a change to the protocol rules, resulting in a divergence in the blockchain.
43. What is a Bitcoin Dust Attack?
A Bitcoin dust attack involves sending tiny amounts of Bitcoin to a wallet to de-anonymize the owner.
44. What is a Bitcoin Testnet?
A Bitcoin testnet is a testing environment for the Bitcoin network, separate from the main blockchain.
45. What is a Bitcoin Orphan Block?
A Bitcoin orphan block is a block that is not included in the main blockchain.
46. What is a Bitcoin Double Spend?
A Bitcoin double spend occurs when someone tries to send the same Bitcoin to two different addresses.
47. What is a Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (BIP)?
A Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (BIP) is a design document for introducing new features or information to Bitcoin.
48. What is a Bitcoin Full Node?
A Bitcoin full node is a program that fully validates transactions and blocks on the Bitcoin network.
49. What is Bitcoin SegWit?
Bitcoin SegWit (Segregated Witness) is an implemented protocol upgrade intended to provide protection from transaction malleability and increase block capacity.
50. What is a Bitcoin Altcoin?
A Bitcoin altcoin is any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. They are called “altcoins” as they are seen as alternatives to Bitcoin.