Imagine being able to harness the power of nature to heat your home in the winter and cool it in the summer. Sounds pretty cool, right? Well, that’s exactly what heat pumps do! In this article, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of heat pump diagrams and help you understand how these incredible devices work.
If you’ve ever wondered how heat pumps manage to extract warmth from the air outside and bring it inside your home during chilly winter days, you’re in the right place. We’ll break down the intricate components and show you how they all fit together like puzzle pieces.
So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey into the inner workings of heat pumps, strap in and get ready to have your mind blown! By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of heat pump diagrams and the magic behind their ability to provide year-round comfort for your humble abode.
Heat Pump Diagrams: Knowing How They Work
- Begin with a basic understanding of the heat pump’s components.
- Study the outdoor unit, which includes the compressor, condenser coil, and fan.
- Explore the indoor unit, consisting of the evaporator coil, air handler, and blower fan.
- Learn about the refrigerant flow, where heat transfer occurs.
- Discover how the heat pump operates in both heating and cooling modes.
- Knowing the role of the thermostat in controlling the system.
- Gain insights into the cycle of heat exchange to achieve desired indoor temperatures.
Basics of Heat Pumps
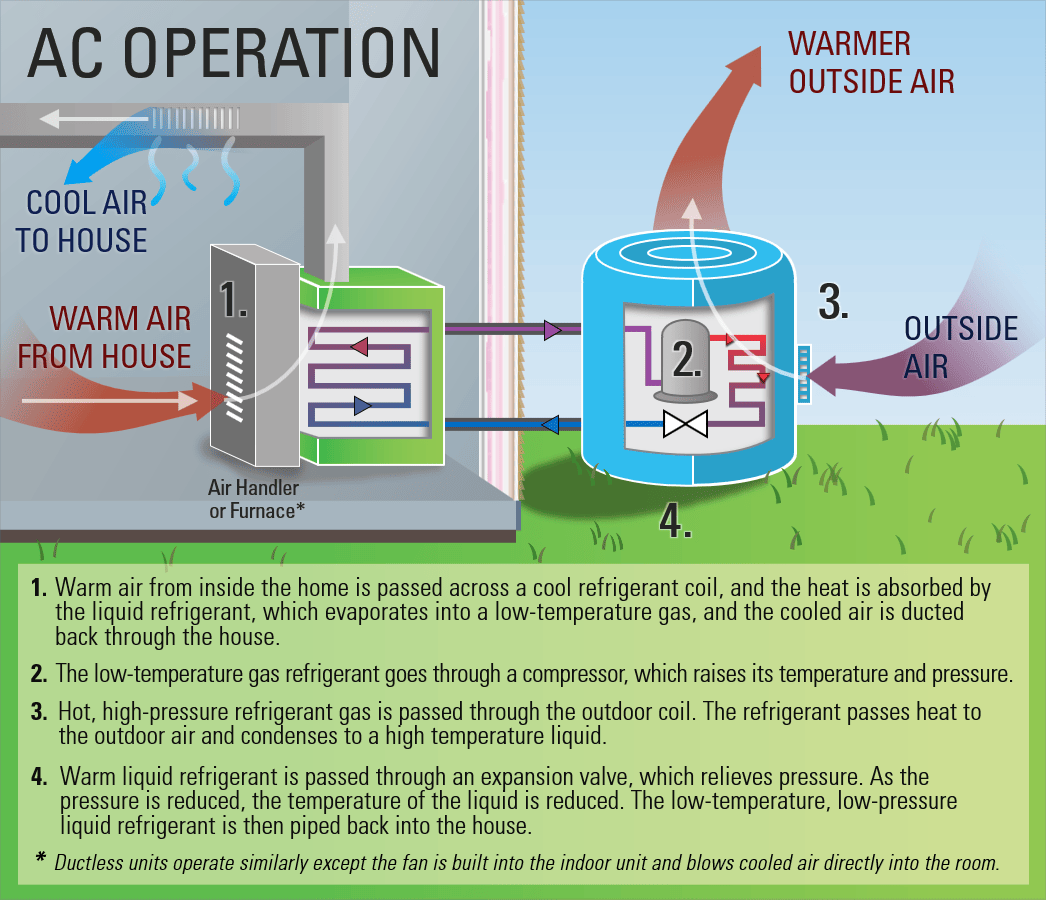
Before we delve into the diagrams, let’s first understand the basics of heat pumps. A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one place to another by using a refrigerant. It can either extract heat from the air, ground, or water to warm your space during colder months or remove heat from your indoor air to provide cooling during hotter months.
The process of heat transfer is facilitated by four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.
In heating mode, the outdoor unit absorbs heat energy from the environment and transfers it to the indoor unit. The refrigerant, a substance that readily changes between gas and liquid states, plays a crucial role in this process. By cycling through the different components, heat pumps can efficiently heat or cool your living space.
Heat pump diagrams visually represent the flow of the refrigerant and the processes involved in heating and cooling. They provide a comprehensive overview of the system, from the outdoor unit to the indoor unit, and help in understanding how each component contributes to the overall operation.
Knowing the Heat Pump Diagram
Heat pump diagrams consist of a variety of symbols that represent different parts and operations. Some common symbols include a compressor, condenser, evaporator, expansion valve, fan, and piping. These symbols help to depict the flow of the refrigerant and the direction of heat transfer.
Let’s break down the different components illustrated in a typical heat pump diagram:
Compressor
The compressor is the heart of the heat pump system. It pressurizes the refrigerant, raising its temperature and increasing its energy. This high-pressure gas is then sent to the condenser for further processing.
In the diagram, the compressor is represented by a triangle-shaped symbol. The arrows indicate the direction of the refrigerant flow.
Condenser
The condenser is responsible for transferring heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air or water. As the high-pressure gas flows through the condenser, it releases heat and turns into a high-pressure liquid.
In the diagram, the condenser is depicted by a rectangular-shaped symbol with zigzag lines inside, representing the transfer of heat to the surrounding environment.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is a small device that regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to expand and turn into a low-pressure gas.
In the diagram, the expansion valve is represented by a triangle or diamond-shaped symbol, depending on the specific diagram.
Evaporator
The evaporator is responsible for absorbing heat from the indoor air or external sources, such as the ground or water. As the low-pressure gas flows through the evaporator, it absorbs heat and turns into a low-pressure vapor.
In the diagram, the evaporator is depicted by a rectangular-shaped symbol with zigzag lines inside, representing the absorption of heat.
Other Components
A heat pump diagram may also include additional components such as a fan, which assists in the exchange of heat, and piping, which carries the refrigerant between the different components.
These components work together in a cyclical process, allowing the heat pump to provide efficient heating and cooling throughout the year. By understanding the diagram and the functions of each component, you can gain a better grasp of how your heat pump system operates.
Benefits of Understanding Heat Pump Diagrams
Why is it important to understand heat pump diagrams? Let’s explore some benefits:
Troubleshooting
By having a clear understanding of the heat pump system and its components, you can troubleshoot any issues that may arise. When a problem occurs, you can identify the faulty component based on the diagram and take appropriate measures to rectify the issue.
For example, if your heat pump is not providing sufficient heating, you can refer to the diagram and check if there is an issue with the compressor or the outdoor unit. This knowledge can save you time and money by avoiding unnecessary service calls.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficient performance of your heat pump system. By referring to the heat pump diagram, you can understand the different parts that require maintenance and when to schedule it.
For instance, the condenser coils may need cleaning to ensure proper heat transfer, or the compressor may require lubrication for smooth operation. By following the diagram, you can create a maintenance checklist and keep your heat pump in optimal condition.
Upgrades and System Design
If you are planning to upgrade your heat pump system or designing a new one, understanding the diagrams is essential. It helps you select the appropriate components and ensure that the system is designed for maximum efficiency and performance.
For example, you can determine the ideal size and capacity of the heat pump based on your heating and cooling requirements. By referring to the diagram, you can assess the compatibility of different components and make informed decisions.
Tips for Understanding Heat Pump Diagrams
Here are some tips to enhance your understanding of heat pump diagrams:
Research and Study
Take the time to research and study different heat pump diagrams. Familiarize yourself with the symbols used and their meanings. There are numerous online resources, books, and manuals available that provide detailed explanations of heat pump diagrams.
By investing time in learning about heat pump diagrams, you can become proficient in interpreting and analyzing them.
Seek Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about any aspect of the heat pump diagram or need assistance with troubleshooting or system design, it is always advisable to seek professional help. HVAC technicians and experts can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their experience and knowledge.
They can explain complex diagrams, identify issues, and suggest appropriate solutions. Don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals when needed.
Understand Your Specific System
Each heat pump system may have slight variations in components and design. It is important to refer to the specific diagram provided by the manufacturer for your system. This ensures accuracy and prevents any confusion or misinterpretation.
By studying the diagram specific to your heat pump, you can fully understand its unique configuration and operation.
Heat Pump Efficiency: Maximizing Performance and Energy Savings
Now that we have explored heat pump diagrams and gained a deeper understanding of how they work, let’s focus on maximizing the efficiency of your heat pump system. Efficient operation not only provides optimal comfort but also helps you save on energy bills. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Proper Sizing
Ensuring that your heat pump is properly sized for your space is crucial for efficient operation. An oversized or undersized heat pump can lead to decreased performance and increased energy consumption.
Work with a professional HVAC contractor to determine the appropriate size of the heat pump based on factors such as square footage, insulation, and climate conditions. A properly sized heat pump will operate efficiently and deliver the desired heating and cooling capacity.
2. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your heat pump in top-notch condition. Schedule professional maintenance at least once a year to clean the coils, check refrigerant levels, inspect electrical connections, and ensure optimal system performance.
Additionally, remember to clean or replace air filters regularly to maintain proper airflow and prevent dust and debris buildup. A well-maintained heat pump operates more efficiently and has a longer lifespan.
3. Smart Thermostat Integration
Enhance the efficiency of your heat pump system by integrating it with a programmable or smart thermostat. These thermostats allow you to set schedules, adjust temperature settings remotely, and optimize energy usage.
By programming your heat pump to operate at lower temperatures when you’re away or asleep, you can save on energy bills without sacrificing comfort. Smart thermostats can also adapt to your preferences and learn your heating and cooling patterns for even greater efficiency.
Knowing heat pump diagrams is essential for troubleshooting, maintenance, and system design. By studying the diagrams and familiarizing yourself with the components and processes involved, you can become more knowledgeable about your heat pump system. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, maximize performance, and achieve energy savings. Take the time to explore heat pump diagrams and unlock the secrets behind efficient heating and cooling!
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will explore heat pump diagrams and understand how they work to provide heating and cooling in buildings. Get ready to unravel the mysteries of heat pump technology!
1. How does a heat pump work?
A heat pump operates by transferring heat from one place to another. It uses a refrigerant that absorbs heat from a cold source, like the outside air or the ground, and then releases that heat inside the building.
This refrigerant flows through a closed-loop system that consists of an outdoor unit (the heat source), an indoor unit (the heat sink), and a compressor. The compressor pumps the refrigerant and increases its temperature, allowing it to release the heat indoors. In the summer, the process reverses, and the heat pump can cool the building by taking heat from inside and releasing it outside.
The heat pump’s ability to move heat instead of generating it makes it an energy-efficient heating and cooling system, as it can produce more heat energy than the electrical energy it consumes. This makes it a great alternative to traditional heating methods.
2. What are the main components of a heat pump system?
A heat pump system consists of several key components. First, there’s the outdoor unit, which contains the compressor, condenser coil, and fan. The outdoor unit extracts heat from the air or ground and transfers it to the refrigerant.
It also releases excess heat generated during the compression process. The indoor unit, on the other hand, includes the evaporator coil and a fan that blows air over it. This coil absorbs heat from the refrigerant, releasing it into the room.
Additionally, a heat pump system has a refrigerant, which is a chemical compound that circulates between the indoor and outdoor units. It goes through a continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation to transfer heat.
There’s also a reversing valve that helps switch the direction of the refrigerant flow, allowing the heat pump to provide both heating and cooling. Lastly, a thermostat is used to control the temperature settings and regulate the heat pump’s operation.
3. Can a heat pump work efficiently in cold climates?
Yes, heat pumps can work efficiently in cold climates. While it may seem counterintuitive, heat pumps can extract heat even from freezing outdoor air. Modern heat pump systems are designed to operate effectively in temperatures as low as –15 to -20 degrees Celsius (-5 to -4 degrees Fahrenheit).
They achieve this by using advanced refrigerants and improved compressor technology that can handle colder conditions. However, it’s important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump decreases as the outdoor temperature drops. In extremely cold climates, supplemental heating may be required to meet higher heat demands.
In regions with severe winters, heat pumps can be equipped with a backup heating system, such as electric resistance heaters or a furnace. These auxiliary systems activate when the heat pump’s efficiency drops below a certain threshold, ensuring that the building stays warm even during the coldest weather.
4. Are there different types of heat pump systems?
Yes, there are different types of heat pump systems available. The most common types are air-source heat pumps, ground-source (geothermal) heat pumps, and water-source heat pumps.
Air-source heat pumps extract heat from the outdoor air. They are popular due to their relatively lower installation costs and ease of maintenance. Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the relatively constant temperature of the earth beneath the surface to transfer heat. They are highly efficient but often come with a higher upfront cost. Water-source heat pumps extract heat from a water source such as a lake, river, or well.
5. How can heat pump diagrams help with troubleshooting?
Heat pump diagrams can be invaluable tools when troubleshooting issues. They offer a visual representation of the system’s components and the flow of refrigerant. By examining the diagram, technicians can identify potential problem areas, such as blocked filters or leaks in the refrigerant lines.
Diagrams also help in understanding the sequence of operations and the interaction between different components, making it easier to pinpoint the root cause of any performance issues. Additionally, heat pump diagrams provide a reference for proper installation and maintenance, ensuring that the system operates effectively and efficiently.
If you’re experiencing issues with your heat pump, consulting the manufacturer’s diagram or seeking guidance from a professional technician can greatly assist in diagnosing and resolving the problem.
So, here’s a quick summary of what we’ve learned about heat pump diagrams:
Heat pumps are like magic machines that can both heat and cool your home. They work by transferring heat from one place to another. In the winter, they pull heat from the outside air and move it inside to warm your home. In the summer, they do the opposite—they remove heat from inside your home and release it outside to keep you cool.
There are two main types of heat pump diagrams: air-source and ground-source. Air-source heat pumps use the air as their heat source or heat sink, while ground-source heat pumps use the ground or water as their heat source or heat sink.
Each type has its advantages and is effective in different climates. Understanding these diagrams can help you see how heat pumps work and how they keep your home comfortable all year round.
So, be thankful for these amazing heat pump machines that keep us warm in winter and cool in summer!






